We provide real 1Z0-821 exam questions and answers braindumps in two formats. Download PDF & Practice Tests. Pass Oracle 1Z0-821 Exam quickly & easily. The 1Z0-821 PDF type is available for reading and printing. You can print more and practice many times. With the help of our Oracle 1Z0-821 dumps pdf and vce product and material, you can easily pass the 1Z0-821 exam.
NEW QUESTION 1
Which five statements describe options available for installing the Oracle Solaris 11operating system using the installation media?
- A. You can perform a text or LiveCD installation locally or over the network.
- B. The text Installer does not install the GNOME deskto
- C. The GNOME desktop package must he added after you have installed the operating system.
- D. The LiveCD Installation cannot be used to install multiple instances of Oracle Solaris.
- E. The LiveCD installer cannot be used if you need to preserve a specific Solaris Volume Table of Contents (VTOC) slice in your current operating system.
- F. The LiveCD Installer is for x86 platforms only.
- G. The GUI installer cannot be used to upgrade your operating system from Solaris 10.
- H. If you are installing Oracle Solaris 11 on an x86-based system that will have more than one operating system installed in it, you cannot partition your disk during the installation process.
- I. The LiveCD installer can be used for SPARC or x86 platforms.
Answer: ABDFH
Explanation:
A: If the network is setup to perform automated installations, you can perform a text installation over the network by setting up an install service on the network and selecting a text installation when the client system boots.
B: After a fresh install of Solaris 11 express, only the console mode is activated. To add Gnome, simply do :
$ sudo pkg install slim_install
This will install additional packages that are not installed by default. D: The text installer advantages over the GUI installer include:
* In addition to modifying partitions, the text installer enables you to create and modify VTOC slices within the Solaris partition.
F: How do I upgrade my Solaris 10 or lower systems to Solaris 11?
Unfortunately, you CAN'T. There is no direct upgrade installer or other tool that will allow you to upgrade from earlier releases of Solaris to Solaris 11. This is primarily due to the vast changes in the packaging mechanism in Solaris 10.
NEW QUESTION 2
You are setting up an automated installer (AI) install server and issue the following command:
installadm create-service -n prod_ai -s /repo/prod_ai.iso
-i 192.168.1.100 -c 5 -d /export/repo
Which four options describe the install server that you have configured?
- A. The service name is prod_ai.
- B. DHCP base IP address is 192.168.1.100
- C. The initial IP address for the install clients will be 192.168.1.100. This IP address is temporar
- D. After the client is booted, it will use IP addresses in the following range: 192.168.1.101-105.
- E. Five IP addresses are allocated for DHCP clients, starting with 192.168.1.100.
- F. The Install server will support up to five clients.
- G. The AI net image ISO file is located in /repo/prod and the net image ISO will be unpacked in /export/repo.
- H. The AI net image ISO file is located in /repo/repo and is named /repo/prod/_ai.iso.
Answer: ABDF
Explanation:
A: -n <svcname>
Uses this install service name instead of default service name.
B: -i <dhcp_ip_start>
Sets up a new DHCP server. The IP addresses, starting from dhcp_address_start, are set up.
D: -c <count_of_ipaddr>
Sets up a total number of IP addresses in the DHCP table equal to the value of the count_of_ipaddr. The first IP address is the value of dhcp_ip_start that is provided by the -i option.
F: -s <srcimage>
Specifies location of AI ISO image to use for setting up the install service.
<targetdir>
Required: Specifies location to set up net image.
NEW QUESTION 3
The following image properties are displayed on your system:
Which two options describe the boot environment policy property that is currently set for this image?
- A. All package operations are performed in a new BE set as active on the next boot.
- B. Do not create a new B
- C. The install, update, uninstall, or revert operation is not performed if a new BE is required.
- D. If a BE is created, do not set it as the active BE on the next boot
- E. A reboot is required for all package operations
- F. A reboot is not required after a package operation.
- G. For package operations that require a reboot, this policy creates a new BE set as active on the next boot.
Answer: DF
Explanation:
Image properties described below.
* be-policy
Specifies when a boot environment is created during packaging operations. The following values are allowed:
/ default
Apply the default BE creation policy: create-backup.
/ always-new (D, F)
Require a reboot for all package operations (D) by performing them in a new BE set as active on the next boot (F). A backup BE is not created unless explicitly requested.
This policy is the safest, but is more strict than most sites need since no packages can be added without a reboot.
NEW QUESTION 4
In an effort to reduce storage space on your server, you would like to eliminate duplicate copies of data in your server’s ZFS file systems.
How do you specify that pool1/data should not contain duplicate data blocks (redundant data) on write operations?
- A. zfs create - o compression=on pool1/data
- B. zpool create -o deduplication =on pool1; zfs create pool1/data
- C. zfs create - o deduplication=on pool1; zfs create pool1/data
- D. zfs create - o dedupratio=2 pool1/data
- E. zfs create - o dedup=on pool1/data
Answer: E
Explanation:
ZFS Deduplication Property
Solaris Express Community Edition, build 129: In this Solaris release, you can use the deduplication property to remove redundant data from your ZFS file systems. If a file system has the dedup property enabled, duplicate data blocks are removed synchronously. The result is that only unique data is stored and common components are shared between files.
You can enable this property as follows:
# zfs set dedup=on tank/home
NEW QUESTION 5
Which two are true about accounts, groups, and roles in the Solaris user database?
- A. All Solaris user accounts must have a unique UID number.
- B. A Solaris account name may be any alphanumeric string, and can have a maximum length of 8 characters.
- C. Account UID numbers 0-09 are system-reserved.
- D. The GID for an account determines the default group ownership of new files created by that account.
- E. The groups that an account is a member of are determined by the entries in the/etc/group file.
Answer: AB
Explanation:
A: Solaris uses a UID (User ID) to identify each user account. The UID is a unique number assigned to each user. It is usually assigned by the operating system when the account is created.
B: In Solaris the account name can include any alphanumeric string (and . _ -). The maximum length is 8 characters.
NEW QUESTION 6
How are operating system updates distributed in the Oracle Solaris 11 environment?
- A. Updates are only available to customers with an active support contrac
- B. The updates are distributed through the My Oracle Support web portal and installed in a central locatio
- C. All software packages are then updated manually from the command line using the smpatch command.
- D. Patches are download from http: //support.oracle.com either automatically or manuall
- E. All software packages are then updated manually from the command line using the smpatch or patchadd commands.
- F. Software updates are published as packages to a repositor
- G. All software packages are then updated manually from the command line using the pkg command.
- H. Software updates, published as packages to an OS imag
- I. All software packages are then updated manually from the command line using the pkg command.
Answer: C
Explanation:
* Updating all of the packages on your installed system – To update all of the packages on your system that have available updates, use the pkg update command, as follows:
# pkg update
Running this command updates packages that you might not otherwise consider updating, for example, kernel components and other low-level system packages.
* Adding or updating individual packages – To add individual software packages, use the pkg install command. Any dependent packages are also updated at the same time.
* install package updates that deliver fixes– A pkg update operation might include bug fixes, so the operation is similar to applying a specific patch or patches in previous Oracle Solaris releases.
Note: The IPS interfaces first check for updates for currently installed packages before retrieving them via the network. By default, interfaces check repository catalogs in the following locations:
* The default installation repository at pkg.oracle.com/solaris/release.
* The support repository in My Oracle Support. This repository is restricted to users with Oracle Solaris 11 Express support contracts, and it contains packages with the latest bug fixes. For this reason, a support contract must be purchased for production deployments.
NEW QUESTION 7
You created a new zpool. Now you need to migrate the existing ZFS file system from pool1/prod to pool2/prod.
You have these requirements:
1. Users must have access to the data during the migration, so you cannot shutdown the file system while the migration takes place.
2. Because you want to copy the data as quickly as possible, you need to increase the server resources devoted to the ZFS migration.
Which method would you use to modify the ZFS shadow migration daemon defaults to increase the concurrency and overall speed of migration?
- A. Svccfg - s filesystem/shadowd:defaultsetprop config_params/shadow_threads=integer: 16endsvcadm refresh filesystem/shadowd: default
- B. Specify the -b <blocksize> option with the zfs create command and increase the value of<blocksize>
- C. Use the -o -volblocksize=<blocksize>option with the zfs create command and increase the value of the default <blocksize>.
- D. Svccfg -s filesystem/zfs: defaultsetprop config_params/shadow_threads = integer: 16endsvcadm refresh filesystem/zfs:default
Answer: A
Explanation:
shadowd is a daemon that provides background worker threads to migrate data for a shadow migration. A shadow migration gradually moves data from a source file system into a new “shadow” file system. Users can access and change their data within the shadow file system while migration is occurring.
The shadowd service is managed by the service management facility, smf(5).
Administrative actions on this service, such as enabling, disabling, or requesting restart, can be performed using svcadm(1M). The service's status can be queried using the svcs(1) command.
The svccfg(1M) command can be used to manage the following parameter related to shadowd:
config_params/shadow_threads
Note: Oracle Solaris 11: In this release, you can migrate data from an old file system to a new file system while simultaneously allowing access and modification of the new file system during the migration process.
Setting the shadow property on a new ZFS file system triggers the migration of the older data. The shadow property can be set to migrate data from the local system or a remote system with either of the following values:
file:///path nfs://host:path
NEW QUESTION 8
When setting up Automated Installer (AI) clients, an interactive tool can be used to generate a custom system configuration profile. The profile will specify the time zone, data and time, user and root accounts, and name services used for an AI client installation. This interactive tool will prompt you to enter the client information and an SC profile (XML) will be created.
Which interactive tool can be used to generate this question configuration?
- A. sys-unconfig
- B. installadm set-criteria
- C. sysconfig create-profile
- D. installadm create-profile
Answer: B
Explanation:
Use the installadm set-criteria command to update the client criteria associated with an AI manifest that you already added to a service using installadm add-manifest.
Use the installadm add-manifest command to add a custom AI manifest to an install service.
The value of manifest is a full path and file name with .xml extension. The manifest file contains an AI manifest (installation instructions). The manifest file can also reference or embed an SC manifest (system configuration instructions).
NEW QUESTION 9
View the Exhibit and review the zpool and ZFS configuration information from your system.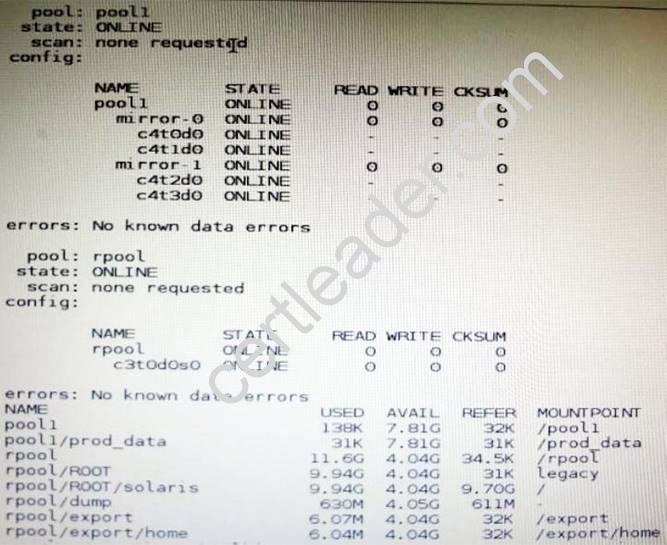
Identify the correct procedure for breaking the /prod_data mirror, removing c4t0d0 and c4t2d0, and making the data on c4t0d0and c4t2d0 accessible under the dev_data mount point.
- A. zpool split pool1 pool2 c4t0d0 c4t2d0zpool import pool2zfs set mountpoint = /dev_data pool2/prod_data
- B. zpool detach pool1 pool2zpool attach pool2zfs set mountpoint=/dev_data pool2/prod_data
- C. zpool split pool1/prod_data -n pool2/dev_datazfs set mountpoint = /dev_data pool2/prod_data
- D. zpool split pool1 pool2 c4t0d0 c4t2d0zpool import pool2
Answer: D
Explanation:
In this Solaris release, you can use the zpool split command to split a mirrored storage pool, which detaches a disk or disks in the original mirrored pool to create another identical pool.
After the split operation, import the new pool.
NEW QUESTION 10
You have a ZFS file system named /dbase/oral and you want to guarantee that 10 GB of storage space is available to that dataset for all data, snapshots, and clones.
Which option would you choose?
- A. zfs set refreservation=10g dbase/oral
- B. zfs set quota=10g dbase/oral
- C. zfs set refquota=10g dbase/oral
- D. zfs set reservation=10g dbase/oral
Answer: D
Explanation:
A ZFS reservation is an allocation of disk space from the pool that is guaranteed to be available to a dataset. As such, you cannot reserve disk space for a dataset if that space is not currently available in the pool. The total amount of all outstanding, unconsumed reservations cannot exceed the amount of unused disk space in the pool. ZFS reservations can be set and displayed by using the zfs set and zfs get commands. For example:
# zfs set reservation=5G tank/home/bill
# zfs get reservation tank/home/bill NAME PROPERTY VALUE SOURCE
tank/home/bill reservation 5G local
NEW QUESTION 11
User jack on host solaris attempts to use ssh to log in to host oracle and receives this message:
jack@solaris:~$ ssh oracle
ssh: connect to host oracle port 22: connection refused What is the problem?
- A. Host oracle does not have a valid host public key.
- B. Host oracle does not have a valid host private key.
- C. Host solaris does not have a valid host public key.
- D. Host does not have a valid host private key.
- E. Host solaris is not configured for host-based authentication.
- F. Host oracle is not configured for host-based authentication.
- G. Host oracle is not running the ssh service.
- H. Host solaris is not running the ssh service.
Answer: G
Explanation:
The host he is trying to connect to (oracle) is not running the required service (ssh).
NEW QUESTION 12
You have set up the task.max-lwps resource control on your Solaris 11 system.
Which option describes how to configure the system so that syslogd notifies you when the resources control threshold value for the task.max-lwps resource has been exceeded?
- A. Use the rctladm command to enable the global action on the task.max-lwpa resource control.
- B. Modify the /etc/syslog.conf file to activate system logging of all violations of task.max- lwps and then refresh then svc: /system/system-log:default service.
- C. Activate system logging of all violations of task.max-lwpp in the /etc/rctldm.conf file and then execute the rctladm-u command.
- D. Use the prct1 command to set the logging of all resource control violations at the time the task.max-lwps resource control is being setup.
- E. Use the setrct1 command to set the logging of all resource control violations for the task.max-lwps resource control.
Answer: A
Explanation:
rctladm - display and/or modify global state of system resource controls
The following command activates system logging of all violations of task.max-lwps.
# rctladm -e syslog task.max-lwps
#
NEW QUESTION 13
You need to install the solaris-desktop group package. Which command would you use to list the set of packages included in that software group?
- A. pkg search
- B. pkg info
- C. pkginfo
- D. pkg contents
Answer: A
Explanation:
Use the pkg search command to search for packages whose data matches the specified pattern.
Like the pkg contents command, the pkg search command examines the contents of packages. While the pkg contents command returns the contents, the pkg search
command returns the names of packages that match the query.
NEW QUESTION 14
You are planning group names for a new system. You decide to use a numbering convention that includes the year and month the project began, to form the group number and name for work associated with that project.
So, for example, a project targeted to begin in January, 2013 would have the number (name):
201301(Pr20l301)
What are the two problems with your plan?
- A. Group names may not contain a numeric character
- B. Group names may be no longer than 7 characters.
- C. Group numbers should not be larger than 60000.
- D. Group names should be all lowercase.
Answer: CD
Explanation:
C: The Group ID (GID) field contains the group's numerical ID. GIDs can be assigned whole numbers between 100 and 60000.
D: Group names contain only lowercase characters and numbers.
NEW QUESTION 15
You want to deploy Oracle Solaris 11 with the Automated Installer (AI). You need to make sure that your server and network meet the requirements for using AI.
Identify two requirements for using AI.
- A. You should set up DHC
- B. The DHCP server and AI install server can be the same machine or two different machines.
- C. You can create only one manifest per install servic
- D. If you need more than one manifest, you should create multiple install services.
- E. The minimum requirement to operate as an AI install server is 1 GB of memory.
- F. If two client machines have different architectures and need to be installed with the same version of the Oracle Solaris 11 OS, then you should create two AI manifests and a single install service.
Answer: AD
Explanation:
A: An automated installation of a client over the network consists of the following high-level steps:
Step 1. The client system boots over the network and gets its network configuration and the location of the install server from the DHCP server.
Step 2: The install server provides a boot image to the client. Etc.
D: If two client machines need to be installed with the same version of the Oracle Solaris 11 OS but need to be installed differently in other ways, then create two AI manifests for the AI install service. The different AI manifests can specify different packages to install or a different slice as the install target, for example.
NEW QUESTION 16
Before booting testzone, a non-global zone, you want to connect to the zone's console so that you can watch the boot process.
Choose the command used xo connect to testzone's console.
- A. zoneadm – C testzone
- B. zoneadm – console testzone
- C. zlogin – z testzone console
- D. zlogin – z testzone – C
- E. zlogin – C testzone
- F. zoneadm – z testzone – C
Answer: E
NEW QUESTION 17
You notice that the /var/.dm/messages file has become very large. Typically, this is managed by a crontab entry. Which entry should be in the root's crontab file?
- A. 10 3 * * * /usr/adm/messages
- B. 10 3 * * * /usr/sbin/logadm
- C. 10 3 * * * /usr/sbin/syslogrotate
- D. 10 3 * * * /usi/sbin/logrotate
- E. 10 3 * * * /usr/sbin/messages
Answer: B
Explanation:
This example shows how to display the default root crontab file.
$ suPassword:
# crontab -l
#ident "@(#)root 1.19 98/07/06 SMI" /* SVr4.0 1.1.3.1 */
#
# The root crontab should be used to perform accounting data collection.
#
#
10 3 * * * /usr/sbin/logadm
15 3 * * 0 /usr/lib/fs/nfs/nfsfind
30 3 * * * [ -x /usr/lib/gss/gsscred_clean ] && /usr/lib/gss/gsscred_clean
#10 3 * * * /usr/lib/krb5/kprop_script slave_kdcs
NEW QUESTION 18
The su command by default makes an entry into the log file for every su command attempt. The following is a single line from the file:
SU 12/18 23:20 + pts/1 user1-root What does the + sign represent?
- A. unsuccessful attempt
- B. successful attempt
- C. The attempt was from a pseudo terminal, and not the console.
- D. The attempt was from a user that is in the adm group, same as root.
- E. Time zone is not set.
Answer: B
Explanation:
The sulog file, /var/adm/sulog, is a log containing all attempts (whether successful or not) of the su command. An entry is added to the sulog file every time the su command is executed. The fields in sulog are: date, time, successful (+) or unsuccessful (-), port, user executing the su command, and user being switched to. In the preceding example, all su attempts were successful, except for the attempt on 2/23 at 20:51, when user pete unsuccessfully attempted to su to user root.
Look for entries where an unauthorized user has used the command inappropriately. The following entry shows a successful (indicated by +) su from user userid to root.
SU 03/31 12:52 + pts/0 <userid>-root
NEW QUESTION 19
When issuing the zonestat 2 1h is command, the following information is displayed: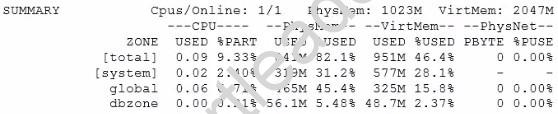
Which two options accurately describe the statistics contained in the output?
- A. dbzone is using 0.21% of the total CPU resource available in the zone's processor set.
- B. dbzone is using 0.21% of the global zone's total CPU.
- C. dbzone is using 5.48% of the total physical memory that has been allocated to the zone.
- D. dbzone is using 2.37% of the global zone's total virtual memory.
- E. The network is being utilized 100% with no physical bandwidth remaining.
Answer: AC
Explanation:
A: %PART
The amount of cpu used as a percentage of the total cpu in a processor-set to which the zone is bound. A zone can only have processes bound to multiple processor sets if it is the global zone, or if psrset(1m) psets are used. If multiple binding are found for a zone, it's
%PART is the fraction used of all bound psets. For [total] and [system], %PART is the percent used of all cpus on the system.
Note: The zonestat utility reports on the cpu, memory, and resource control utilization of the currently running zones. Each zone's utilization is reported both as a percentage of system resources and the zone's configured limits.
The zonestat utility prints a series of interval reports at the specified interval. It optionally also prints one or more summary reports at a specified interval.
NEW QUESTION 20
User jack makes use of the bash shell; his home directory is/export/home/jack.
What is the correct setting of umask, and where should it be set, to allow jack to create a shell script using the vi editor, that is executable by default?
- A. It is not possible to make a script executable without using the chmod command.
- B. umask value of 0002 set in /etc/profile
- C. umask value of 0002 set in /export/home/jack/.bashrc
- D. umask value of 0722 set in /etc/profile
- E. umask value of 0722 set In /export/home/jack/.bashrc
Answer: B
Explanation:
The user file-creation mode mask (umask) is use to determine the file permission for newly created files. It can be used to control the default file permission for new files. It is a four- digit octal number.
You can setup umask in /etc/bashrc or /etc/profile file for all users. By default most Unix distro set it to 0022 (022) or 0002 (002).
1. The default umask 002 used for normal user. With this mask default directory permissions are 775 and default file permissions are 664.
2. The default umask for the root user is 022 result into default directory permissions are 755 and default file permissions are 644.
3. For directories, the base permissions are (rwxrwxrwx) 0777 and for files they are 0666 (rw-rw-rw).
In short,
1. A umask of 022 allows only you to write data, but anyone can read data.
2. A umask of 077 is good for a completely private system. No other user can read or write your data if umask is set to 077.
3. A umask of 002 is good when you share data with other users in the same group. Members of your group can create and modify data files; those outside your group can read data file, but cannot modify it. Set your umask to 007 to completely exclude users who are not group members.
NEW QUESTION 21
You have a user that needs to use the cron tool to schedule some repetitive tasks. When the user enters the crontab –e command in a terminal window, the following error appears:
crontab: you are not authorized to use cron. Sorry
In order to troubleshoot this issue, in what directory would you start your invest
- A. /etc/cron.d
- B. /var/spool/cron
- C. /var/spool/cron/crontable
- D. /var/spool/cron/atjobs
Answer: A
Explanation:
crontab: you are not authorized to use cron. Sorry.
This message means that either the user is not listed in the cron.allow file (if the file exists), or the user is listed in the cron.deny file.
You can control access to the crontab command by using two files in the /etc/cron.d directory: cron.deny and cron.allow. These files permit only specified users to perform crontab command tasks such as creating, editing, displaying, or removing their own crontab files.
The cron.deny and cron.allow files consist of a list of user names, one user name per line.
NEW QUESTION 22
After installing the OS, you boot the system and notice that the syslogd daemon is not
accepting messages from remote systems.
Which two options should you select to modify the syslogd daemon configuration so that it accepts messages from remote systems?
- A. svccfg -s svc:/system/system -log setprop start/exec= “syslogd -t”Restart the syslogd daemon.
- B. Set the following parameter in the /etc/syslogd.conf file: LOG_FROM_REMOTE= YESRestart the syslogd daemon.
- C. svcadm enable svc:/system/system -log/config/log_from_remoteRestart the syslogd daemon.
- D. svccfg -s svc:/system/system-log setprop config/log_from_remote=trueRestart the syslogd daemon.
- E. Set the following parameter in the /etc/default/syslogd file: LOG_FROM_REMOTE=YESRestart the syslogd daemon.
Answer: BD
Explanation:
B: The /etc/default/syslogd file contains the following default parameter settings. See FILES.
LOG_FROM_REMOTE
Specifies whether remote messages are logged. LOG_FROM_REMOTE=NO is equivalent to the -t command-line option. The default value for LOG_FROM_REMOTE is YES.
NEW QUESTION 23
Review the storage pool information: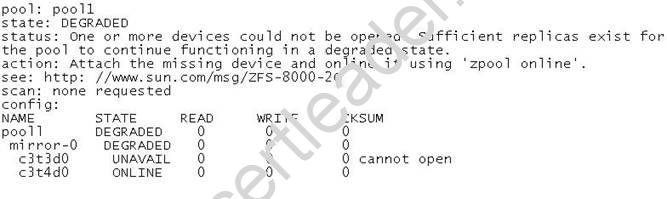
Choose the correct procedure to repair this storage pool.
- A. Shut the system down, replace disk c3t3d0, and boot the syste
- B. When the system is booted, execute the zpool clear pool1 command.
- C. Shut the system down, replace disk c3t3d0, and boot the syste
- D. When the system is booted execute the zpool online pool1 command.
- E. Shut the system down, replace disk c3t3d0, and boot the syste
- F. When the system is booted, execute the zpool replace pool1 c3t3d0 command.
- G. Shut the system down, replace disk c3t3d0, and boot the syste
- H. When the system is booted, execute the zpool replace pool1 c3t3d0 c3t3d0 command.
Answer: C
Explanation:
You might need to replace a disk in the root pool for the following reasons: The root pool is too small and you want to replace it with a larger disk
The root pool disk is failing. In a non-redundant pool, if the disk is failing so that the system won't boot, you'll need to boot from an alternate media, such as a CD or the network, before you replace the root pool disk.
In a mirrored root pool configuration, you might be able to attempt a disk replacement without having to boot from alternate media. You can replace a failed disk by using the zpool replace command.
Some hardware requires that you offline and unconfigure a disk before attempting the zpool replace operation to replace a failed disk.
For example:
# zpool offline rpool c1t0d0s0
# cfgadm -c unconfigure c1::dsk/c1t0d0
<Physically remove failed disk c1t0d0>
<Physically insert replacement disk c1t0d0>
# cfgadm -c configure c1::dsk/c1t0d0
# zpool replace rpool c1t0d0s0
# zpool online rpool c1t0d0s0
# zpool status rpool
<Let disk resilver before installing the boot blocks>
SPARC# installboot -F zfs /usr/platform/`uname -i`/lib/fs/zfs/bootblk /dev/rdsk/c1t0d0s0 x86# installgrub /boot/grub/stage1 /boot/grub/stage2 /dev/rdsk/c1t9d0s0
NEW QUESTION 24
You suspect a problem with the oponldap package and want to make sure that the files have not be modified or otherwise tampered with.
Which command would validate all of the files contained in the openldap package and report any problems?
- A. pkgchk openldap
- B. pkginfo openldap
- C. pkg contents openldap
- D. pkg verify openldap
- E. pkg set-property signature-policy verify
Answer: A
Explanation:
pkgchk checks the accuracy of installed files or, by using the -l option, displays information about package files. pkgchk checks the integrity of directory structures and files. Discrepancies are written to standard error along with a detailed explanation of the problem.
NEW QUESTION 25
The COMSTAR framework provides support for the iSCSI protocol. Select three options that correctly describe the COMSTAR framework.
- A. iSCSI devices can be used as dump devices.
- B. SCSI commands are carried over IP networks and enable you to mount disk devices from across the network onto your local system.
- C. Large amounts of data can be transferred over an IP network with very little network degradation.
- D. COMSTAR allows you to convert any Solaris11 host into a SCSI target device that can be accessed over a storage network.
- E. One IP port can handle multiple ISCSI target devices.
Answer: BDE
Explanation:
B: By carrying SCSI commands over IP networks, the iSCSI protocol enables you to access block devices from across the network as if they were connected to the local system. COMSTAR provides an easier way to manage these iSCSI target devices.
D: Common Multiprotocol SCSI TARget, or COMSTAR, a software framework that enables you to convert any Oracle Solaris 11 host into a SCSI target device that can be accessed over a storage network by initiator hosts.
E: One IP port can handle multiple iSCSI target devices.
NEW QUESTION 26
In order to display the IP addresses of network interfaces, what command would you use?
- A. dladm
- B. ipconfig
- C. sves
- D. ipadm
- E. ipaddr
Answer: D
Explanation:
'ipadm show-addr' displays all the configured addresses on the system. Example:
# ipadm show-addr
ADDROBJ TYPE STATE ADDR
lo0/v4 static ok 127.0.0.1/8 lo0/v6 static ok ::1/128
NEW QUESTION 27
You are troubleshooting a newly installed desktop Oracle Solaris 11 system with a single network interface. From this system, you can connect to other systems within the company
intranet, but cannot access any external services (such as websites and email), even when using IP addresses.
Examining the routing table confirms that the default route to 192.168.1.1 is missing. DHCP is not used at this site. Which two commands will temporarily mid permanently configure the default route?
- A. ipadm set-gateway 192.168.1.1
- B. route add default 192.168.1.1
- C. ipadm set-default 192.168.1.1
- D. dladm route-add –d 192.168.1.1
- E. echo 192.168.1.1 >/etc/gateway
- F. echo 192.168.1.1 >/etc/defaultrouter
Answer: BF
Explanation:
B: Setting the default route on Solaris is easy. If you are trying to just set the route temporarily you can use the route command:
Route add default <ipaddress> Example:
Route add default 192.168.1.1
Note: Route command manipulates the kernel routing tables. Routing is the process of forwarding a packet from one computer to another. It is based on the IP address in the IP packet header and netmask.
F: If you want the route to be persisted when you reboot the system, you will need to set the route in the /etc/defaultrouter file.
/etc/defaultrouter Example:
Echo 192.168.1.1 > /etc/defaultrouter
NEW QUESTION 28
You run the command dlstat show-link -r.
Select the two correct statements regarding the information displayed in the INTRS column.
- A. No value is listed for virtual network interfaces.
- B. A value of 0 is listed for virtual interfaces and ether stubs.
- C. The number of Interrupts is listed, which indicates network efficiency.
- D. A number equal to the number of transmitted Ethernet frames is listed for physical links.
- E. The number of packets that were interrupted by a collision is listed, which may indicate hardware problems.
Answer: CE
Explanation:
In this output, the statistics for interrupt (INTRS) are significant. Low interrupt numbers indicate greater efficiency in performance. If the interrupt numbers are high, then you might need to add more resources to the specific link.
Example:
# dlstat -r -i 1
LINK IPKTS RBYTES INTRS POLLS CH<10 CH10-50 CH>50 e1000g0 101.91K 32.86M 87.56K 14.35K 3.70K 205 5
nxge1 9.61M 14.47G 5.79M 3.82M 379.98K 85.66K 1.64K vnic1 8 336 0 0 0 0 0
e1000g0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
nxge1 82.13K 123.69M 50.00K 32.13K 3.17K 724 24
vnic1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Note: dlstat show-link [-r [-F] | -t] [-i interval] [-a] [-p] [ -o field[, ...]] [-u R|K|M|G|T|P] [link] Display statistics for a link.
-r
Display receive-side statistics only. Includes bytes and packets received, hardware and software drops, and so forth.
List of supported RX fields: link
iusedby
ibytes ipkts intrs polls
hdrops: hardware drops
sdrops: software drops (owing to bandwidth enforcement) ch<10: number of packet chains of length < 10
ch10-50: number of packet chains of length between 10 and 50 ch>50: number of packet chains of length > 50
NEW QUESTION 29
Before booting test zone a non-global zone, you want to connect to the zone’s console so that you can watch the boot process.
Choose the command used to connect to testzone’s console.
- A. zoneadm -C testzone
- B. zoneadm -console testzone
- C. zlogin - z testzone console
- D. zlogin - z testzone - C
- E. zlogin -C testzone
- F. zoneadm - testzone - c
Answer: E
Explanation:
The following options are supported:
C
Connects to the zone console. Connects to the zone console.
Note:
After you install a zone, you must log in to the zone to complete its application environment. You might log in to the zone to perform administrative tasks as well. Unless the -C option is used to connect to the zone console, logging in to a zone
using zlogin starts a new task. A task cannot span two zones
NEW QUESTION 30
The current ZFS configuration on your server is:
pool1 124K 3.91G 32K /pool1 pool1/data 31K 3.91G 31K /data
You need to create a new file system named /data2. /data2 will be a copy of the /data file system.
You need to conserve disk space on this server whenever possible.
Which option should you choose to create /data2, which will be a read writeable copy of the
/data file system, while minimizing the amount of total disk space used in pool1?
- A. zfs set mountpoint=/data2 compression=on pool1/data2
- B. zfs snapshot pool1/data@nowzfs set mountpoint=/data2, comptession=on pool1/data@now
- C. zfs create snapshot pool1/data@nowzfs send pool1/data@now | zfs recv pool1/data2
- D. zfs create snapshot pool1/data@nowzfs clone -o mountpoint=/data2 pool1/data@now pool1/data2
- E. zfs snapshot pool1/data@nowzfs clone -o mountpoint=/data2 -ocompression=on pool1/data@now pool1/data2
- F. zfs snapshot pool1/data@nowzfs clone -o mountpoint=/data2 pool1/data@now pool1/data2
Answer: E
Explanation:
zfs snapshot [-r] [-o property=value] ... filesystem@snapname|volume@snapname Creates a snapshot with the given name. All previous modifications by successful system calls to the file system are part of the snapshot
zfs clone [-p] [-o property=value] ... snapshot filesystem|volume Creates a clone of the given snapshot.
Note:
Because snapshots are fast and low overhead, they can be used extensively without great concern for system performance or disk use .
With ZFS you can not only create snapshot but create a clone of a snapshot.
A clone is a writable volume or file system whose initial contents are the same as the dataset from which it was created. As with snapshots, creating a clone is nearly instantaneous, and initially consumes no additional disk space. In addition, you can snapshot a clone.
A clone is a writable volume or file system whose initial contents are the same as the original dataset. As with snapshots, creating a clone is nearly instantaneous, and initially consumes no additional space.
Clones can only be created from a snapshot. When a snapshot is cloned, it creates an implicit dependency between the parent and child.
NEW QUESTION 31
......
P.S. Easily pass 1Z0-821 Exam with 243 Q&As Dumpscollection Dumps & pdf Version, Welcome to Download the Newest Dumpscollection 1Z0-821 Dumps: http://www.dumpscollection.net/dumps/1Z0-821/ (243 New Questions)
