Certleader offers free demo for 1z0-1085-20 exam. "Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Foundations 2020 Associate", also known as 1z0-1085-20 exam, is a Oracle Certification. This set of posts, Passing the Oracle 1z0-1085-20 exam, will help you answer those questions. The 1z0-1085-20 Questions & Answers covers all the knowledge points of the real exam. 100% real Oracle 1z0-1085-20 exams and revised by experts!
Free demo questions for Oracle 1z0-1085-20 Exam Dumps Below:
NEW QUESTION 1
What do the terms OpEx and CapEx refer to?
- A. OpEx refers to Operational Excellence and CapEx refers to Capital Excellence
- B. OpEx refers to Operational Expenditure and CapEx refers to Capital Expenditure
- C. OpEx refers to Operational Expansion and CapEx refers to Capital Expenses
- D. OpEx refers to Operational Example and CapEx refers to Capita Example
Answer: B
Explanation:
CapEx is Capital expenditures comprise major purchases that will be used in the future.
OpEx Operating expenditures (expenses) represent day-to-day costs that are necessary to keep a business running.
NEW QUESTION 2
Which is NOT required to register and log support requests in My Oracle Support (MOS)?
- A. Your Customer Support Identifier (CSl)
- B. Your account password
- C. Your tenancy OCID (Oracle Cloud Identifier)
- D. Your resource OCID (Oracle Cloud Identifier)
Answer: D
Explanation:
You can open a support service request with Oracle Support To create a service request:
Go to My Oracle Support and sign in.
If you are not signed in to Oracle Cloud Support, click Switch to Cloud Support at the top of the page. Click Create Service Request.
Select the following from the displayed menus:
Service Type: Select Oracle Cloud Infrastructure from the list. Service Name: Select the appropriate option for your organization. Problem Type: Select your problem type from the list.
Enter your contact information.
Enter a Description, and then enter the required fields specific to your issue. For most Oracle Cloud Infrastructure issues you need to include the OCID (Oracle Cloud Identifier) for each resource you need help with. See Locating Oracle Cloud Infrastructure IDs for instructions on locating these.
NEW QUESTION 3
Which is a key benefit of using oracle cloud infrastructure autonomous data warehouse?
- A. No username and password required
- B. Scale both CPU and Storage without downtime
- C. Apply database patches as they become available
- D. Maintain root level acress to the underlying operating system
Answer: B
Explanation:
Oracle Autonomous Data Warehouse is a cloud data warehouse service that eliminates virtually all the complexities of operating a data warehouse and securing data. It automates provisioning, configuring, securing, tuning, scaling, patching, backing up, and repairing of the data warehouse. Unlike other “fully managed” cloud data warehouse solutions that only patch and update the service, it also features elastic, automated scaling, performance tuning, security, and a broad set of built-in capabilities that enable machine learning analysis, simple data loading, and data visualizations.
Data Warehouse uses continuous query optimization, table indexing, data summaries, and auto-tuning to ensure consistent high performance even as data volume and number of users grows. Autonomous scaling can temporarily increase compute and I/O by a factor of three to maintain performance. Unlike other cloud services which require downtime to scale, Autonomous Data Warehouse scales while the service continues to run.
NEW QUESTION 4
Which service level agreement type is NOT offered by Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Compute service?
- A. Data Plane
- B. Performance
- C. Application Plane
- D. Control Plane
Answer: C
Explanation:
Oracle offers several different service level agreements as defined in this section (Service Level Agreements).Service level agreements range from least restrictive (data plane) to more restrictive (control plane) to most restrictive (performance).
NEW QUESTION 5
A customer wants to use Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) storing application backups which can be stored for months, but retrieved immediately based on business needs. Which OCI storage service can be used to meet this requirement?
- A. Archive Storage
- B. Block Volume
- C. Object Storage (standard)
- D. File Storage
Answer: C
Explanation:
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure offers two distinct storage class tiers to address the need for both performant, frequently accessed "hot" storage, and less frequently accessed "cold" storage. Storage tiers help you maximize performance where appropriate and minimize costs where possible.
Use Object Storage for data to which you need fast, immediate, and frequent access. Data accessibility and performance justifies a higher price to store data in the Object Storage tier.
Use Archive Storage for data to which you seldom or rarely access, but that must be retained and preserved f long periods of time. The cost efficiency of the Archive Storage tier offsets the long lead time required to access the data.
Unlike Object Storage, Archive Storage data retrieval is not instantaneous.
NEW QUESTION 6
Which three methods can you use to create or modify Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) resources?
- A. REST APIs
- B. OCI desktop client
- C. Secure Shell (SSH)
- D. OCI Console
- E. Command-line Interface
- F. Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP)
- G. Serial console connection
Answer: ADE
Explanation:
You can create and manage resources in the following ways:
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure ConsoleThe Console is an intuitive, graphical interface that lets you create and manage your instances, cloud networks, and storage volumes, as well as your users and permissions.
See Using the Console.
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure APIsThe Oracle Cloud Infrastructure APIs are typical REST APIs that use HTTPS requests and responses. See API Requests.
SDKsSeveral Software Development Kits are available for easy integration with the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure APIs, including SDKs for Java, Ruby, and Python. For more information, see Developer Resources.
Command Line Interface (CLI)You can use a command line interface with some services. For more information, see Developer Resources.
TerraformOracle supports Terraform. Terraform is "infrastructure-as-code" software that allows you to define your infrastructure resources in files that you can persist, version, and share. For more information, see Getting Started with the Terraform Provider.
AnsibleOracle supports the use of Ansible for cloud infrastructure provisioning, orchestration, and configuration management. Ansible allows you to automate configuring and provisioning your cloud infrastructure, deploying and updating software assets, and orchestrating your complex operational processes. For more information, see Getting Started with Ansible for Oracle Cloud Infrastructure.
Resource ManagerResource Manager is an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure service that allows you to automate the process of provisioning your Oracle Cloud Infrastructure resources. It helps you install, configure, and manage resources using the "infrastructure-as-code" model. For more information, see Overview of Resource Manager.
NEW QUESTION 7
You are required to host several files in a location that can be publicly accessible from anywhere in the world. Which Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) service should you use?
- A. OCI Object Storage
- B. Oracle Functions
- C. OCI Block Volume
- D. OCI File Storage
- E. OCI Storage Gateway
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 8
Which Oracle Cloud Infrastructure compute shapes does not incur instance billing in a STOPPED state?
- A. Dense I/O
- B. Standard
- C. GPU
- D. HPC
Answer: B
Explanation:
A shape is a template that determines the number of CPUs, amount of memory, and other resources that are allocated to an instance.
Standard shapes don't incur costs in a STOPPED state.
NEW QUESTION 9
According to Shared security model, which two are a customer's responsibilities in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI)?
- A. Physical security of OCI data center facilities
- B. Virtual Machine hypervisor
- C. Local NVMe data persistence
- D. Customer data
- E. Object Storage data durability
Answer: DE
Explanation:
Customer and Oracle's responsibilities can be divided into the following areas:
Physical Security: Oracle is responsible for protecting the global infrastructure that runs all of the services offered in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. This infrastructure consists of the hardware, software, networking, and facilities that run Oracle Cloud Infrastructure services.
Identity and Access Management (IAM): As with all Oracle cloud services, you should protect your cloud access credentials and set up individual user accounts. You are responsible for managing and reviewing access for your own employee accounts and for all activities that occur under your tenancy. Oracle is responsible for providing effective IAM services such as identity management, authentication, authorization, and auditing.
Workload Security: You are responsible for protecting and securing the operating system and application layers of your compute instances from attacks and compromises. This protection includes patching applications and operating systems, operating system configuration, and protection against malware and network attacks. Oracle is responsible for providing secure images that are hardened and have the latest patches. Also, Oracle makes it simple for you to bring the same third-party security solutions that you use today.
Data Classification and Compliance: You are responsible for correctly classifying and labeling your data and meeting any compliance obligations. Also, you are responsible for auditing your solutions to ensure that they meet your compliance obligations.
Host Infrastructure Security: You are responsible for securely configuring and managing your compute (virtua
hosts, containers), storage (object, local storage, block volumes), and platform (database configuration) services. Oracle has a shared responsibility with you to ensure that the service is optimally configured and secured. This responsibility includes hypervisor security and the configuration of the permissions and network access controls required to ensure that hosts can communicate correctly and that devices are able to attach or mount the correct storage devices.
Network Security: You are responsible for securely configuring network elements such as virtual networking, load balancing, DNS, and gateways. Oracle is responsible for providing a secure network infrastructure.
Client and Endpoint Protection: Your enterprise uses various hardware and software systems, such as mobile devices and browsers, to access your cloud resources. You are responsible for securing all clients and endpoints that you allow to access Oracle Cloud Infrastructure services.
NEW QUESTION 10
Which two security capabilities are offered by Oracle Cloud Infrastructure?
- A. Always on data encryption for data-at-rest.
- B. Certificate Management service
- C. Captcha
- D. Key Management service
- E. Managed Active Directory service
Answer: AD
Explanation:
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure’s security approach is based on seven core pillars. Each pillar has multiple solutions designed to maximize the security and compliance of the platform and to help customers to improve their security posture.
High Availability: Offer fault-independent data centers that enable high-availability scale-out architectures and are resilient against network attacks, ensuring constant uptime in the face of disaster and security attack.
Customer Isolation: Allow customers to deploy their application and data assets in an environment that commits full isolation from other tenants and Oracle’s staff.
Data Encryption: Protect customer data at-rest and in-transit in a way that allows customers to meet the security and compliance requirements with respect to cryptographic algorithms and key management.
Security Controls: Offer customers effective and easy-to-use application, platform, and network security solutions that allow them to protect their workloads, have a secure application delivery using a global edge network, constrain access to their services, and segregate operational responsibilities to reduce the risk associated with malicious and accidental user actions.
Visibility: Offer customers comprehensive log data and security analytics that they can use to audit and monitor actions on their resources, allowing them to meet their audit requirements and reduce security and operational risk.
Secure Hybrid Cloud: Enable customers to use their existing security assets, such as user accounts and policies, as well as third-party security solutions, when accessing their cloud resources and securing their data and application assets in the cloud.
Verifiably Secure Infrastructure: Follow rigorous processes and use effective security controls in all phases of cloud service development and operation. Demonstrate adherence to Oracle’s strict security standards through third-party audits, certifications, and attestations. Help customers demonstrate compliance readiness to internal security and compliance teams, their customers, auditors, and regulators.
NEW QUESTION 11
Which kind of scaling is supported by virtual machines in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Compute service?
- A. Only scaling up or down
- B. Only scaling out
- C. Scaling up or down, and scaling in or out
- D. Only scaling in
Answer: C
Explanation:
Horizontal scaling means that you scale by adding more machines into your pool of resources
whereas Vertical scaling means that you scale by adding more power (CPU, RAM) to an existing machine.
An easy way to remember this is to think of a machine on a server rack, we add more machines across the horizontal direction and add more resources to a machine in the vertical direction.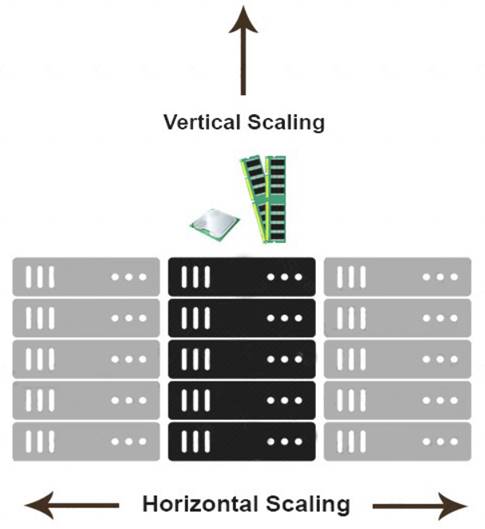
With horizontal-scaling it is often easier to scale dynamically by adding more machines into the existing pool
— Vertical-scaling is often limited to the capacity of a single machine, scaling beyond that capacity often involves downtime and comes with an upper limit.
NEW QUESTION 12
Which option provides the best performance for running OTLP workloads in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI)?
- A. OCI Autonomous Data Warehouse
- B. OCI Virtual Machine Instance
- C. OCI Dedicated Virtual Host
- D. OCI Autonomous Transaction Processing
Answer: D
Explanation:
https://docs.oracle.com/en/cloud/paas/atp-cloud/index.html
NEW QUESTION 13
You are setting up a proof of concept (POC) and need to quickly establish a secure between an on-premises data center and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI).
Which OCI service should you implement?
- A. VCN Peering
- B. FastConnect
- C. Internet Gateway
- D. IPSec VPN
Answer: D
Explanation:
You can set up a single IPSec VPN with a simple layout that you might use for a proof of concept (POC).
NEW QUESTION 14
You have a mission-critical application which requires to be globally available at all times. Which deployment strategy should you adopt?
- A. Use multiple Fault Domains In each Availability Domain in each Region.
- B. Use multiple Availability Domains In one Region.
- C. Use multiple Fault Domains In one Region.
- D. Use multiple Fault Domains in any Availability Domain in multiple Regions.
Answer: A
Explanation:
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure is hosted in regions and availability domains. A region is a localized geographic area, and an availability domain is one or more data centers located within a region. A region is composed of one or more availability domains.
Regions are independent of other regions and can be separated by vast distances—across countries or even continents.
Availability domains are isolated from each other, fault tolerant, and very unlikely to fail simultaneously. Because availability domains do not share infrastructure such as power or cooling, or the internal availability domain network, a failure at one availability domain within a region is unlikely to impact the availability of the others within the same region.
Fault domain is a grouping of hardware and infrastructure within an availability domain. Each availability domain contains three fault domains. Fault domains provide anti-affinity: they let you distribute your instances so that the instances are not on the same physical hardware within a single availability domain. A hardware failure or Compute hardware maintenance event that affects one fault domain does not affect instances in other fault domains. In addition, the physical hardware in a fault domain has independent and redundant power supplies, which prevents a failure in the power supply hardware within one fault domain from affecting other fault domains.
NEW QUESTION 15
Which Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) service is best suited for running serverless apps?
- A. Oracle Functions
- B. Virtual Cloud Network
- C. Streaming
- D. Audit
Answer: A
Explanation:
Oracle Functions is a fully managed, multi-tenant, highly scalable, on-demand, Functions-as-a-Service platform. It is built on enterprise-grade Oracle Cloud Infrastructure and powered by the Fn Project open source engine. Use Oracle Functions (sometimes abbreviated to just Functions) when you want to focus on writing code to meet business needs.
The serverless and elastic architecture of Oracle Functions means there's no infrastructure administration or software administration for you to perform. You don't provision or maintain compute instances, and operating system software patches and upgrades are applied automatically. Oracle Functions simply ensures your app is highly-available, scalable, secure, and monitored. With Oracle Functions, you can write code in Java, Python, Node, Go, and Ruby (and for advanced use cases, bring your own Dockerfile, and Graal VM). You can then deploy your code, call it directly or trigger it in response to events, and get billed only for the resources consumed during the execution.
Oracle Functions is based on Fn Project. Fn Project is an open source, container native, serverless platform that can be run anywhere - any cloud or on-premises. Fn Project is easy to use, extensible, and performant. You can download and install the open source distribution of Fn Project, develop and test a function locally, and then use the same tooling to deploy that function to Oracle Functions.
You can access Oracle Functions using the Console, a CLI, and a REST API. You can invoke the functions you deploy to Oracle Functions using the CLI or by making signed HTTP requests.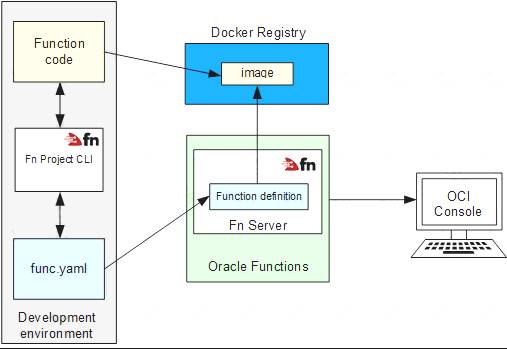
NEW QUESTION 16
Which statement is true for an oracle cloud Infrastructure (OCI) compute instance?
- A. Compute instance always get a public IP address
- B. Compute instance does not use a boot volume
- C. Compute instance cannot leverage auto scaling feature
- D. Compute instance always get a private IP address
Answer: D
Explanation:
When you create an instance, the instance is automatically attached to a virtual network interface card (VNIC) in the cloud network's subnet and given a private IP address from the subnet's CIDR. You can let the IP address be automatically assigned, or you can specify a particular address of your choice. The private IP address lets instances within the cloud network communicate with each other.
NEW QUESTION 17
OCI budgets can be set on which two options?
- A. Cost-tracking tags
- B. Free-form tags
- C. Compartments
- D. Virtual Cloud Network
- E. Tenancy
Answer: AC
Explanation:
In OCI a budget can be used to set soft limits on your Oracle Cloud Infrastructure spending. You can set alerts on your budget to let you know when you might exceed your budget, and you can view all of your budgets and spending from one single place in the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure console.
Budgets are set on
· Cost-tracking tags
· Compartments (including the root compartment)
NEW QUESTION 18
______ is a fully-managed, scalable, and highly available service that you can use to deploy your containerized applications to the cloud.
- A. Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Container Engine for Kubernetes
- B. Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Container Engine for Containerization
- C. Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Container Engine for Deployment
- D. Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Container Engine for Docker
Answer: A
Explanation:
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Container Engine for Kubernetes is a fully-managed, scalable, and highly available service that you can use to deploy your containerized applications to the cloud. Use Container Engine for Kubernetes (sometimes abbreviated to just OKE) when your development team wants to reliably build, deploy, and manage cloud-native applications. You specify the compute resources that your applications require, and Container Engine for Kubernetes provisions them on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure in an existing OCI tenancy.
You can access Container Engine for Kubernetes to define and create Kubernetes clusters using the Console and the REST API. You can access the clusters you create using the Kubernetes command line (kubectl), the Kubernetes Dashboard, and the Kubernetes API.
Container Engine for Kubernetes is integrated with Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Identity and Access Management (IAM), which provides easy authentication with native Oracle Cloud Infrastructure identity functionality.
NEW QUESTION 19
Which describes a key benefit of using Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI)?
- A. With OCI, you can only run Java based workloads on bare metal.
- B. With OCI, you can run only cloud-native workloads.
- C. Only bare metal workloads are supported on OCI.
- D. OCI offers consistent performance with a predictable pricing model.
Answer: D
Explanation:
https://www.oracle.com/in/cloud/pricing.html
- OCI offers consistent performance with a predictable pricing model - is the best suited answer.
- Only bare metal workloads are supported in OCI - False, since you can work with VMs etc too
- With OCI, you can run cloud native workloads - False, since you can work with on-premise by connecting it to OCI too.
- With OCI, you can only run Java based workloads on bare metal - False since Java is not the only programming language supported by OCI.
NEW QUESTION 20
A new customer has logged into Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) as an administrator for the first time. The admin would like to deploy Infrastructure into a region other then their home region.
What is the first Stop they must take in order to accomplish this task?
- A. Use API endpoints to create resources in the desired region.
- B. Navigate to the desired region and begin creating resources.
- C. Subscribe to the desired region.
- D. File a service request for access to each additional region.
Answer: C
Explanation:
When you sign up for Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, Oracle creates a tenancy for you in one region. This is your home region. Your home region is where your IAM resources are defined. When you subscribe to another region, your IAM resources are available in the new region, however, the master definitions reside in your home region and can only be changed there.
When you subscribe your tenancy to a new region, all the policies from your home region are enforced in the new region. If you want to limit access for groups of users to specific regions, you can write policies to grant access to specific regions only.
NEW QUESTION 21
you are analyzing your Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) usage with Cost Analysis tool in OCI Console. Which is not a default feature of the tool?
- A. Filter costs by applications
- B. Filter costs by compartments
- C. Filter costs by tags
- D. Filter costs by date
Answer: A
Explanation:
You can filter Costs Analysis Tools by following three ways To filter costs by dates
To filter costs by tags
To filter costs by compartments
NEW QUESTION 22
Which is an example of Edge Services in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI)?
- A. Virtual Cloud Network (VCN)
- B. Object Storage
- C. Web Application Firewall
- D. Virtual Firewall
Answer: C
Explanation:
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Web Application Firewall (WAF) is a cloud-based, Payment Card Industry (PCI compliant, global security service that protects applications from malicious and unwanted internet traffic.
WAF can protect any internet facing endpoint, providing consistent rule enforcement across a customer's
applications.
WAF provides you with the ability to create and manage rules for internet threats including Cross-Site Scripting (XSS), SQL Injection and other OWASP-defined vulnerabilities. Unwanted bots can be mitigated while tactically allowed desirable bots to enter. Access rules can limit based on geography or the signature of the request.
NEW QUESTION 23
A customer wants to use Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) for storing application backups which can be stored based on business needs.
Which OCI storage service can be used to meet the requirement?
- A. File Storage
- B. Block Volume
- C. Archive Storage
- D. Object Storage (standard)
Answer: D
Explanation:
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure offers two distinct storage class tiers to address the need for both performant, frequently accessed "hot" storage, and less frequently accessed "cold" storage. Storage tiers help you maximize performance where appropriate and minimize costs where possible.
1) Use Object Storage for data to which you need fast, immediate, and frequent access. Data accessibility an performance justifies a higher price to store data in the Object Storage tier.
2) Use Archive Storage for data to which you seldom or rarely access, but that must be retained and preserve for long periods of time. The cost efficiency of the Archive Storage tier offsets the long lead time required to access the data. For more information, see Overview of Archive Storage.
The Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage service is an internet-scale, high-performance storage platform that offers reliable and cost-efficient data durability. The Object Storage service can store an unlimited amount
of unstructured data of any content type, including analytic data and rich content, like images and videos.
With Object Storage, you can safely and securely store or retrieve data directly from the internet or from within the cloud platform. Object Storage offers multiple management interfaces that let you easily manage storage at scale. The elasticity of the platform lets you start small and scale seamlessly, without experiencing any degradation in performance or service reliability.
Object Storage is a regional service and is not tied to any specific compute instance. You can access data from anywhere inside or outside the context of the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, as long you have internet connectivity and can access one of the Object Storage endpoints. Authorization and resource limits are discussed later in this topic.
Object Storage also supports private access from Oracle Cloud Infrastructure resources in a VCN through
a service gateway. A service gateway allows connectivity to the Object Storage public endpoints from private IP addresses in private subnets. For example, you can back up DB systems to an Object Storage bucket over the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure backbone instead of over the internet. You can optionally use IAM policies to control which VCNs or ranges of IP addresses can access Object Storage. See Access to Oracle Services: Service Gateway for details.
Object Storage is Always Free eligible. For more information about Always Free resources, including additional capabilities and limitations, see Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Free Tier.
The following list summarizes some of the ways that you can use Object Storage.
NEW QUESTION 24
......
P.S. 2passeasy now are offering 100% pass ensure 1z0-1085-20 dumps! All 1z0-1085-20 exam questions have been updated with correct answers: https://www.2passeasy.com/dumps/1z0-1085-20/ (83 New Questions)
