Want to know Passleader 2V0-41.23 Exam practice test features? Want to lear more about VMware VMware NSX 4.x Professional certification experience? Study Best Quality VMware 2V0-41.23 answers to Leading 2V0-41.23 questions at Passleader. Gat a success with an absolute guarantee to pass VMware 2V0-41.23 (VMware NSX 4.x Professional) test on your first attempt.
Check 2V0-41.23 free dumps before getting the full version:
NEW QUESTION 1
Which three protocols could an NSX administrator use to transfer log messages to a remote log server? (Choose three.)
- A. HTTPS
- B. TCP
- C. SSH
- D. UDP
- E. TLS
- F. SSL
Answer: BDE
Explanation:
An NSX administrator can use TCP, UDP, or TLS protocols to transfer log messages to a remote log server. These protocols are supported by NSX Manager, NSX Edge, and hypervisors for remote logging. A Log Insight log server supports all these protocols, as well as LI and LI-TLS, which are specific to Log Insight and optimize network usage. HTTPS, SSH, and SSL are not valid protocols for remote logging in NSX-T Data Center. References: : VMware NSX-T Data Center Administration Guide, page 102. : VMware Docs: Configure Remote Logging
NEW QUESTION 2
Which three NSX Edge components are used for North-South Malware Prevention? (Choose three.)
- A. Thin Agent
- B. RAPID
- C. Security Hub
- D. IDS/IPS
- E. Security Analyzer
- F. Reputation Service
Answer: BCD
Explanation:
https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-NSX/4.1/administration/GUID-69DF70C2-1769-4858-97E7-B757CAED
NEW QUESTION 3
Which is an advantages of a L2 VPN In an NSX 4.x environment?
- A. Enables Multi-Cloud solutions
- B. Achieve better performance
- C. Enables VM mobility with re-IP
- D. Use the same broadcast domain
Answer: D
Explanation:
L2 VPN is a feature of NSX that allows extending Layer 2 networks across different sites or clouds over an IPsec tunnel. L2 VPN has an advantage of enabling VM mobility with re-IP, which means that VMs can be moved from one site to another without changing their IP addresses or network configurations. This is possible because L2 VPN allows both sites to use the same broadcast domain, which means that they share the same subnet and VLAN .
NEW QUESTION 4
How is the RouterLink port created between a Tier-1 Gateway and Tier-O Gateway?
- A. Automatically created when Tier-1 is connected with Tier-0 from NSX UI.
- B. Automatically created when Tier-1 is created.
- C. Manually create a Logical Switch and connect to bother Tier-1 and Tier-0 Gateways.
- D. Manually create a Segment and connect to both Tier-1 and Tier-0 Gateways.
Answer: A
Explanation:
The RouterLink port is automatically created when a Tier-1 Gateway is connected with a Tier-0 Gateway from the NSX UI1. The RouterLink port is a logical interface that is assigned an IP address and is associated with a physical or virtual interface. The RouterLink port acts as an end point of the IPSec tunnel and routes traffic between the Tier-1 Gateway and the Tier-0 Gateway2. The other options are incorrect because they involve manual creation of logical switches or segments, which are not required for RouterLink port
creation. References: Configure NSX for Virtual Networking from vSphere Client, Virtual Private Networ (VPN)
NEW QUESTION 5
When a stateful service is enabled for the first lime on a Tier-0 Gateway, what happens on the NSX Edge node'
- A. SR is instantiated and automatically connected with DR.
- B. DR Is instantiated and automatically connected with SR.
- C. SR and DR Is instantiated but requites manual connection.
- D. SR and DR doesn't need to be connected to provide any stateful services.
Answer: A
Explanation:
The answer is A. SR is instantiated and automatically connected with DR.
SR stands for Service Router and DR stands for Distributed Router. They are components of the NSX Edge node that provide different functions1
The SR is responsible for providing stateful services such as NAT, firewall, load balancing, VPN, and DHCP. The DR is responsible for providing distributed routing and switching between logical segments and the physical network1
When a stateful service is enabled for the first time on a Tier-0 Gateway, the NSX Edge node automatically creates an SR instance and connects it with the existing DR instance. This allows the stateful service to be applied to the traffic that passes through the SR before reaching the DR2
According to the VMware NSX 4.x Professional Exam Guide, understanding the SR and DR components and their functions is one of the exam objectives3
To learn more about the SR and DR components and how they work on the NSX Edge node, you can refer to the following resources: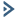 VMware NSX Documentation: NSX Edge Components 1
VMware NSX Documentation: NSX Edge Components 1  VMware NSX 4.x Professional: NSX Edge Architecture
VMware NSX 4.x Professional: NSX Edge Architecture  VMware NSX 4.x Professional: NSX Edge Routing
VMware NSX 4.x Professional: NSX Edge Routing
NEW QUESTION 6
Refer to the exhibit.
Which two items must be configured to enable OSPF for the Tler-0 Gateway in the Image? Mark your answers by clicking twice on the image.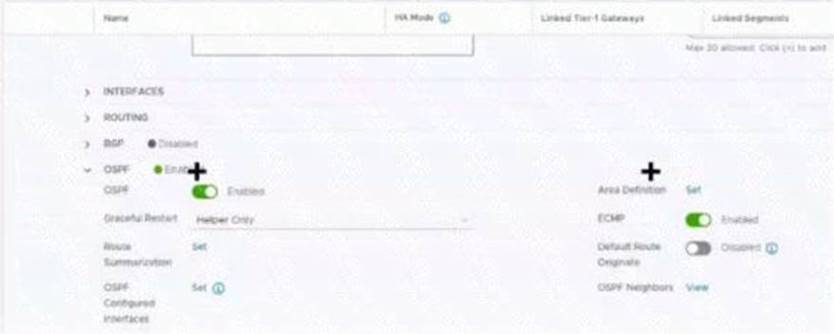
Solution:
The correct answer is to enable the OSPF toggle and to add an Area Definition for the Tier-0 gateway in image. These two items are required to configure OSPF on the Tier-0 gateway, as explained in the web search results123.
To mark your answers by clicking twice on the image, you can double-click on the toggle switch next
to OSPF to turn it on. The switch should change from gray to blue, indicating that the option is enabled. The you can double-click on the Set button next to Area Definition to add an area definition. A pop-up windo should appear where you can specify the area ID and type.
* 1. Click the OSPF toggle to enable OSPF 2. In the Area Definition field, click Set to add an area definition https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-NSX-T-Data-Center/3.2/administration/GUID-5BEC626C-5312-467D-B
Does this meet the goal?
- A. Yes
- B. Not Mastered
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 7
Which CLI command shows syslog on NSX Manager?
- A. get log-file auth.lag
- B. /var/log/syslog/syslog.log
- C. show log manager follow
- D. get log-file syslog
Answer: D
Explanation:
According to the VMware NSX CLI Reference Guide, this CLI command shows the syslog messages on the NSX Manager node. You can use this command to view the system logs for troubleshooting or monitoring purposes.
The other options are either incorrect or not available for this task. get log-file auth.log is a CLI command that shows the authentication logs on the NSX Manager node, not the syslog messages. /var/log/syslog/syslog.log is not a CLI command, but a file path that may contain syslog messages on some Linux systems, but not on the NSX Manager node. show log manager follow is not a valid CLI command, as there is no show log command or manager option in the NSX CLI.
## NSX Cli command get log-file <fiilename>
get log-file <filename> follow
# Below are commonly used log files, there are many more log files
get log-file <auth.log | controller | controller-error | http.log | kern.log | manager.log | node-mgmt.log | policy.log | syslog> [follow]
# use [follow] to continuing monitor Example: get log-file syslog follow get log-file syslog
NEW QUESTION 8
Which TraceFlow traffic type should an NSX administrator use tor validating connectivity between App and DB virtual machines that reside on different segments?
- A. Multicast
- B. Unicast
- C. Anycast
- D. Broadcast
Answer: B
Explanation:
Unicast is the traffic type that an NSX administrator should use for validating connectivity between App and DB virtual machines that reside on different segments. According to the VMware documentation1, unicast traffic is the traffic type that is used to send a packet from one source to one destination. Unicast traffic is the most common type of traffic in a network, and it is used for applications such as web browsing, email, file transfer, and so on2. To perform a traceflow with unicast traffic, the NSX administrator needs to specify the source and destination IP addresses, and optionally the protocol and related parameters1. The traceflow will show the path of the packet across the network and any observations or errors along the way3. The other options are incorrect because they are not suitable for validating connectivity between two specific virtual machines. Multicast traffic is the traffic type that is used to send a packet from one source to multiple destinations simultaneously2. Multicast traffic is used for applications such as video streaming, online gaming and group communication4. To perform a traceflow with multicast traffic, the NSX administrator needs to specify the source IP address and the destination multicast IP address1. Broadcast traffic is the traffic type that is used to send a packet from one source to all devices on the same subnet2. Broadcast traffic is used for applications such as ARP, DHCP, and network discovery. To perform a traceflow with broadcast traffic, the NSX administrator needs to specify the source IP address and the destination MAC address as FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF1. Anycast traffic is not a valid option, as it is not supported by NSX Traceflow. Anycast traffic is a traffic type that is used to send a packet from one source to the nearest or best destination among a group of devices that share the same IP address. Anycast traffic is used for applications such as DNS, CDN, and load balancing.
NEW QUESTION 9
An administrator has connected two virtual machines on the same overlay segment. Ping between both virtual machines is successful. What type of network boundary does this represent?
- A. Layer 2 VPN
- B. Layer 2 bridge
- C. Layer 2 broadcast domain
- D. Layer 3 route
Answer: C
Explanation:
An overlay segment is a logical construct that provides Layer 2 connectivity between virtual machines that are attached to it. An overlay segment can span multiple hosts and can be extended across different subnets or locations using Geneve encapsulation3. Therefore, two virtual machines on the same overlay segment belong to the same Layer 2 broadcast domain, which means they can communicate with each other using their MAC addresses without requiring any routing. The other options are incorrect because they involve Layer 3 or higher network boundaries, which require routing or tunneling to connect different
segments. References: VMware NSX Documentation
NEW QUESTION 10
When running nsxcli on an ESXi host, which command will show the Replication mode?
- A. get logical-switch <Local-Switch-UUID> status
- B. get logical-switch <Logical-Switch-UUID>
- C. get logical-switches
- D. get logical-switch status
Answer: B
NEW QUESTION 11
An NSX administrator Is treating a NAT rule on a Tler-0 Gateway configured In active-standby high availability mode. Which two NAT rule types are supported for this configuration? (Choose two.)
- A. Reflexive NAT
- B. Destination NAT
- C. 1:1 NAT
- D. Port NAT
- E. Source NAT
Answer: BE
Explanation:
According to the VMware NSX Documentation, these are two NAT rule types that are supported for a tier-0 gateway configured in active-standby high availability mode. NAT stands for Network Address Translation and is a feature that allows you to modify the source or destination IP address of a packet as it passes through a gateway. Destination NAT: This rule type allows you to change the destination IP address of a packet from an external IP address to an internal IP address. You can use this rule type to provide access to your internal servers from external networks using public IP addresses.
Destination NAT: This rule type allows you to change the destination IP address of a packet from an external IP address to an internal IP address. You can use this rule type to provide access to your internal servers from external networks using public IP addresses. Source NAT: This rule type allows you to change the source IP address of a packet from an internal IP address to an external IP address. You can use this rule type to provide access to external networks from your internal servers using public IP addresses.
Source NAT: This rule type allows you to change the source IP address of a packet from an internal IP address to an external IP address. You can use this rule type to provide access to external networks from your internal servers using public IP addresses.
NEW QUESTION 12
Refer to the exhibit.
An administrator configured NSX Advanced Load Balancer to redistribute the traffic between the web servers. However, requests are sent to only one server
Which of the following pool configuration settings needs to be adjusted to resolve the problem? Mark the correct answer by clicking on the image.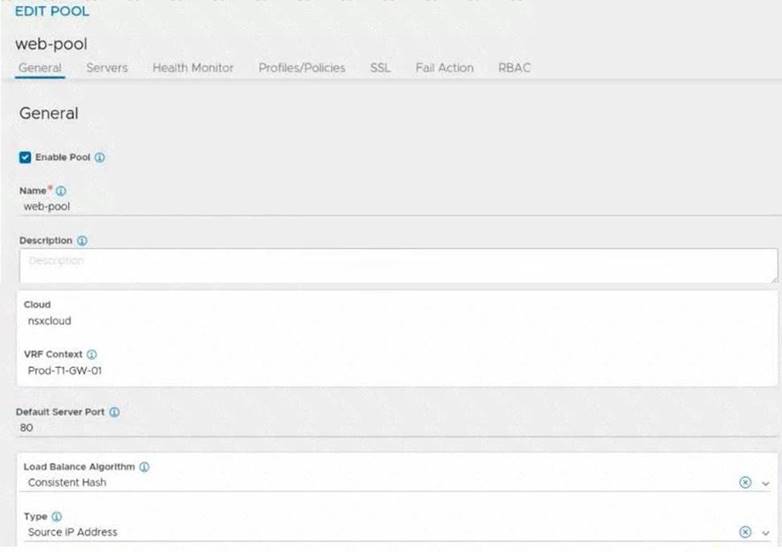
Solution:
Load Balancing Algorithm
Does this meet the goal?
- A. Yes
- B. Not Mastered
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 13
NSX improves the security of today's modern workloads by preventing lateral movement, which feature of NSX can be used to achieve this?
- A. Network Segmentation
- B. Virtual Security Zones
- C. Edge Firewalling
- D. Dynamic Routing
Answer: A
Explanation:
According to the web search results, network segmentation is a feature of NSX that improves the security of today’s modern workloads by preventing lateral movement. Lateral movement is a technique used by attackers to move from one compromised system to another within a network, exploiting vulnerabilities or credentials . Network segmentation prevents lateral movement by dividing a network into smaller segments or zones, each with its own security policies and controls. This way, if one segment is compromised, the attacker cannot access other segments or resources . NSX enables network segmentation by using micro-segmentation, which applies granular firewall rules at the virtual machine level, regardless of the physical network topology .
NEW QUESTION 14
How is the RouterLink port created between a Tier-1 Gateway and Tler-0 Gateway?
- A. Manually create a Logical Switch and connect to bother Tler-1 and Tier-0 Gateways.
- B. Automatically created when Tler-1 is created.
- C. Manually create a Segment and connect to both Titrr-1 and Tier-0 Gateways.
- D. Automatically created when Tier-t Is connected with Tier-0 from NSX UI.
Answer: D
Explanation:
According to the VMware NSX 4.x Professional documents and tutorials, a RouterLink port is a logical port that connects a Tier-1 gateway to a Tier-0 gateway. This port is automatically created when a Tier-1 gateway is associated with a Tier-0 gateway from the NSX UI or API. The RouterLink port enables routing between the two gateways and carries all the routing protocols and traffic. There is no need to manually create a logical switch or segment for this purpose1.
NEW QUESTION 15
Which two of the following features are supported for the Standard NSX Application Platform Deployment? (Choose two.)
- A. NSX Intrusion Detection and Prevention
- B. NSX Intelligence
- C. NSX Network Detection and Response
- D. NSX Malware Prevention Metrics
- E. NSX Intrinsic Security
Answer: CD
Explanation:
The NSX Application Platform Deployment features are divided into three form factors: Evaluation, Standard, and Advanced. Each form factor determines which NSX features can be activated or installed on the platform1. The Evaluation form factor supports only NSX Intelligence, which provides network visibility and analytics for NSX-T environments2. The Standard form factor supports both NSX Intelligence and NSX Network Detection and Response, which provides network threat detection and response capabilities for
NSX-T environments3. The Advanced form factor supports all four features: NSX Intelligence, NSX Network Detection and Response, NSX Malware Prevention, and NSX Metrics1.
https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-NSX-T-Data-Center/3.2/nsx-application-platform/GUID-85CD2728-8081
NEW QUESTION 16
What needs to be configured on a Tler-0 Gateway lo make NSX Edge Services available to a VM on a VLAN-backed logical switch?
- A. Downlink Interface
- B. VLAN Uplink
- C. Loopback Router Port
- D. Service Interface
Answer: B
Explanation:
To make NSX Edge Services available to a VM on a VLAN-backed logical switch, you need to configure
a VLAN Uplink on the Tier-0 Gateway. A VLAN Uplink is a logical interface that connects the Tier-0 Gateway to the physical network and provides external connectivity for the NSX Edge Services1. A VLAN Uplink can be configured on the NSX Manager UI by selecting Networking > Tier-0 Gateways > Interfaces > Set > Add Interface1.
https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-NSX/4.1/administration/GUID-D641380B-4C8E-4C8A-AF64-4261A266
NEW QUESTION 17
When configuring OSPF on a Tler-0 Gateway, which three of the following must match in order to establish a neighbor relationship with an upstream router? (Choose three.)
- A. Naming convention
- B. MTU of the Uplink
- C. Subnet mask
- D. Address of the neighbor
- E. Protocol and Port
- F. Area ID
Answer: BCF
Explanation:
ccording to the VMware NSX Documentation, these are the three parameters that must match in order to establish an OSPF neighbor relationship with an upstream router on a tier-0 gateway: MTU of the Uplink: The maximum transmission unit (MTU) of the uplink interface must match the MTU of the upstream router interface. Otherwise, OSPF packets may be fragmented or dropped, causing neighbor adjacency issues.
MTU of the Uplink: The maximum transmission unit (MTU) of the uplink interface must match the MTU of the upstream router interface. Otherwise, OSPF packets may be fragmented or dropped, causing neighbor adjacency issues. Subnet mask: The subnet mask of the uplink interface must match the subnet mask of the upstream router interface. Otherwise, OSPF packets may not reach the correct destination or be rejected by the upstream router.
Subnet mask: The subnet mask of the uplink interface must match the subnet mask of the upstream router interface. Otherwise, OSPF packets may not reach the correct destination or be rejected by the upstream router. Area ID: The area ID of the uplink interface must match the area ID of the upstream router interface.
Area ID: The area ID of the uplink interface must match the area ID of the upstream router interface.
Otherwise, OSPF packets may be ignored or discarded by the upstream router.
NEW QUESTION 18
An administrator is configuring service insertion for Network Introspection. Which two places can the Network Introspection be configured? (Choose two.)
- A. Host pNIC
- B. Partner SVM
- C. Tier-0 gateway
- D. Tier-1 gateway
- E. Edge Node
Answer: AB
Explanation:
Network Introspection is a service insertion feature that allows third-party network security services to
monitor and analyze the traffic between virtual machines. Network Introspection can be configured on the host pNIC or on the partner SVM, depending on the type of service and the deployment model. The host pNIC configuration is used for services that require traffic redirection from the physical network to the service virtual machine. The partner SVM configuration is used for services that require traffic redirection from the virtual network to the service virtual machine. Network Introspection cannot be configured on the Tier-0 or Tier-1 gateways, as they are not part of the data plane where the service insertion occurs. Network Introspection also cannot be configured on the edge node, as it is a logical construct that hosts the Tier-0 and Tier-1 gateways. References: Distributed Service Insertion, NSX Securing “Anywhere” Part IV
NEW QUESTION 19
Which of the two following characteristics about NAT64 are true? (Choose two.)
- A. NAT64 is stateless and requires gateways to be deployed in active-standby mode.
- B. NAT64 is supported on Tier-1 gateways only.
- C. NAT64 is supported on Tier-0 and Tier-1 gateways.
- D. NAT64 requires the Tier-1 gateway to be configured in active-standby mode.
- E. NAT64 requires the Tier-1 gateway to be configured in active-active mode.
Answer: CD
Explanation:
https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-NSX/4.1/administration/GUID-69604E49-BC8B-4777-BFD8-B98F8D1F
NEW QUESTION 20
......
Thanks for reading the newest 2V0-41.23 exam dumps! We recommend you to try the PREMIUM Surepassexam 2V0-41.23 dumps in VCE and PDF here: https://www.surepassexam.com/2V0-41.23-exam-dumps.html (106 Q&As Dumps)
