We provide real HPE6-A42 exam questions and answers braindumps in two formats. Download PDF & Practice Tests. Pass HP HPE6-A42 Exam quickly & easily. The HPE6-A42 PDF type is available for reading and printing. You can print more and practice many times. With the help of our HP HPE6-A42 dumps pdf and vce product and material, you can easily pass the HPE6-A42 exam.
Check HPE6-A42 free dumps before getting the full version:
NEW QUESTION 1
What is a valid way to deploy an Aruba Mobility Master (MM)?
- A. as a subscription-based service through the Aruba cloud
- B. as a role on a Mobility Controller 7030 that is deployed as a standalone controller
- C. as a virtual appliance on a server that meets the recommended hardware requirements
- D. as a role on a Mobility Controller 7240 that is deployed as a master controller
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 2
A network administrator reduces an AP radio transmit power from 18 dBm to 15 dBm. This is a loss of 3 dBms.
What is the current power as a percentage of the original power?
- A. 10%
- B. 33%
- C. 50%
- D. 83%
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 3
Refer to the exhibit.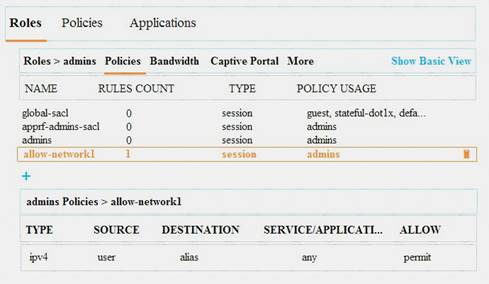
The alias in the rule shown in the exhibit is network 10.1.1.0/24.
A wireless client is assigned IP address 10.1.2.10/24 and the “admins” role. The wireless client at 10.1.2.10 attempts to initiate a Web session with a server at 10.1.1.2. A wired client at 10.1.1.3 attempts to initiate an SSH session with the wireless client at 10.1.2.10.
How does the Aruba firewall handle these attempts?
- A. The firewall drops the traffic from the wireless clien
- B. The firewall drops the traffic from the wired client.
- C. The firewall permits the traffic from the wireless client, but drops the return traffic from the serve
- D. The firewall drops the traffic from the wireless client.
- E. The firewall permits the traffic from the wireless client and also permits the return traffic from the serve
- F. The firewall permits the traffic from the wired client and also permits the return traffic from the wireless client.
- G. The firewall permits the traffic from the wireless client and also permits the return traffic from the serve
- H. The firewall drops the traffic from the wired client.
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 4
Refer to the exhibit.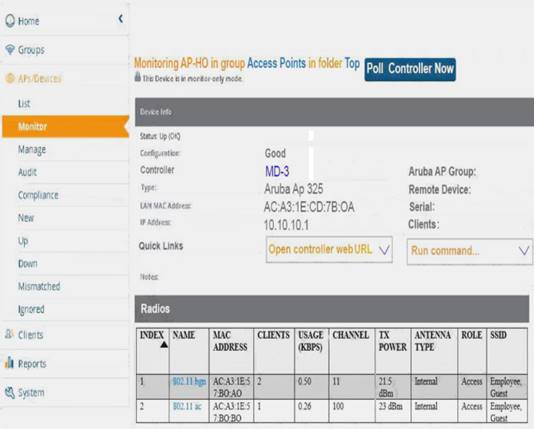
A network administrator needs to use Aruba AirWave to view statistics for an AP’s 802.11ac radio. How can the administrator update the information on-demand rather than wait the typical interval?
- A. Click Poll Controller Now
- B. Click the 802.11ac link
- C. Log out of the interface and log back in
- D. Refresh the browser
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 5
Refer to the exhibit.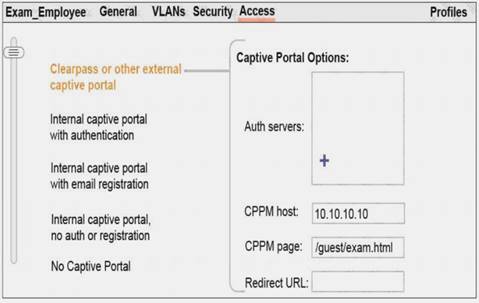
A network administrator creates a guest WLAN on an Aruba Mobility Master (MM). The exhibit shows some of the settings for the WLAN.
How should the network administrator handle the Auth server settings?
- A. Add an authentication server with the LDAP type and the IP address of the company AD server.
- B. Add an authentication server with the LDAP type and IP address 10.10.10.10.
- C. Add an authentication server with the RADIUS type and IP address 10.10.10.10.
- D. Add an authentication server with the RADIUS type and the IP address of the company AD server.
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 6
Refer to the exhibits. Exhibit 1
Exhibit 2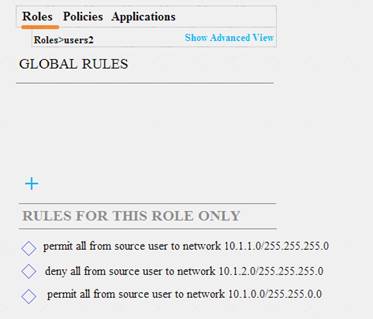
A company has an Aruba solution. Client 1 is assigned to the users1 role, and client 2 is assigned to the users2 role. The exhibits show current firewall rules for those roles. The network1 alias used to be 10.1.1.0/24, but the network administrator now changes the network1 alias to 172.16.1.0/24. Client 1 and Client 2 both send a packet destined to 172.16.1.10.
How does the firewall handle these packets?
- A. It permits the packet from Client 1 and denies the packet from Client 2.
- B. It permits both packets.
- C. It denies the packet from Client 1 and permits the packet from Client 2.
- D. It denies both packets.
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 7
Refer to the exhibit.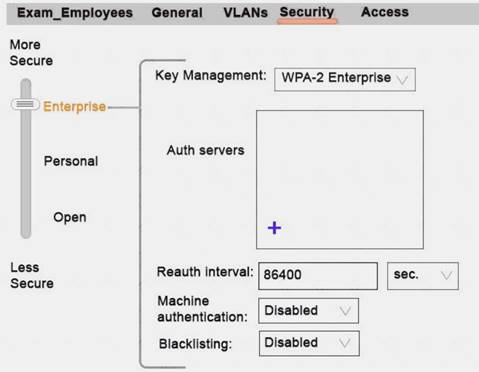
Network administrators need to set up a WLAN that uses WPA2 encryption and authenticates users with a preshared key (PSK) that is the same for all users. Administrators do not see where they should specify the option for the preshared key.
What should the administrators do?
- A. Click Personal in the slide bar.
- B. Click the + icon in the Authentication server section
- C. Return to the first page in the wizard and select the guest option
- D. Configure an L3 authentication profile after the WLAN wizard is complete
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 8
Refer to the exhibit.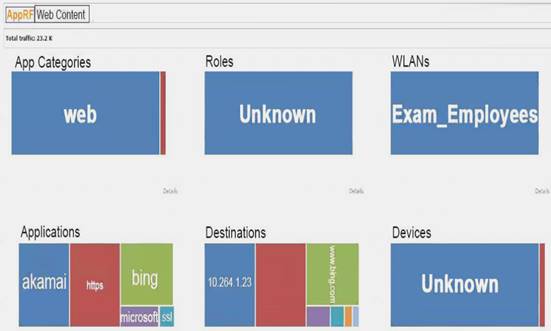
The exhibit shows output from a Mobility Master (MM) dashboard. What is a valid reason for the administrator to click the akamai square under applications?
- A. to create filter rules in order to control wireless user access to this application
- B. to download a report about the usage of this application over time
- C. to see more details about this application, such as a list of aggregated sessions
- D. to see the break down for only roles, destinations, WLANs and devices that use this application
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 9
A company has an Aruba solution. The company wants to support a guest WLAN with the internal captive portal, but the company also wants to develop their own custom portal pages.
What correctly describes the level of customization that the internal captive portal supports?
- A. The internal captive portal must use the default pages without modification, but administrators can upload pages developed externally.
- B. Administrators can modify the default internal captive portal pages, but cannot upload pages developped externally.
- C. Administrators can modify the default internal captive portal pages or upload pages developped externally.
- D. The internal captive portal must use the default pages without modification, and administrators cannot upload pages developped externally.
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 10
A company has an Aruba solution. A network administrator wants to prevent wireless users from accessing shopping web sites with a bad reputation.
What should the administrator set up to deny such traffic?
- A. an AppRF engine
- B. application filters in the Traffic Analysis dashboard
- C. firewall access control rules that specify HTTP and HTTPS services
- D. firewall application rules
Answer: D
NEW QUESTION 11
How does a high-gain omni-directional antenna compare to a typical omni-directional antenna?
- A. it provides more multi-user spatial streams.
- B. it provides more coverage in the horizontal direction than in the vertical direction.
- C. it provides more single-user spatial streams.
- D. it provides more coverage in both the horizontal and vertical directions.
Answer: B
NEW QUESTION 12
A company plans to deploy a Mobility Master (MM) solution with two MM nodes. The MM solution will manage 20 Mobility Controller (MC) appliances that will control a total of 800 APs.
How should the network administrator install the AP licenses?
- A. 40 AP licenses on the MM
- B. 400 AP licenses on the MM
- C. 800 AP licenses on each MC
- D. 800 AP licenses on the MM and 40 AP licenses on each MC
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 13
Refer to the exhibit.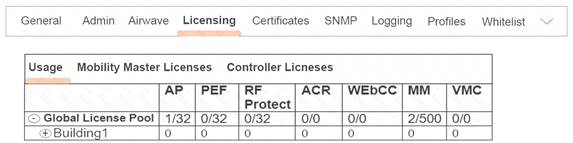
Based on the exhibit, what is the maximum number of APs that this Mobility Master (MM) solution can support?
- A. 1
- B. 32
- C. 500
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 14
Which improvement does ArubaOS 8 offer for the Client Match feature?
- A. It checks the compliance posture for Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) endpoints to improve security.
- B. It enables the application of unique CM rules for specific client types.
- C. It checks client behavior against a wider array of rules to detect more DoS attacks and intrusion attempts.
- D. It offloads client load balancing decisions to local controllers.
Answer: D
NEW QUESTION 15
What is a role fulfilled by an Aruba Mobility Master (MM)?
- A. It forwards and routes traffic for wireless users across multiple sites.
- B. It terminates control tunnels for Aruba APs.
- C. It provides an advanced Web portal for onboarding Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) devices.
- D. It manages VLAN and routing configuration for multiple Mobility Controllers (MCs).
Answer: D
NEW QUESTION 16
A network administrator configures this policy: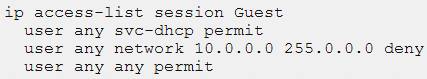
Users to which this policy applies are unable to receive IP addresses with DHCP. How should the administrator fix the issue?
- A. Change user to any in the user any svc-dhcp permit rule.
- B. Move the user any svc-dhcp permit rule to the bottom of the list.
- C. Remove the deny rule from the policy.
- D. Use the correct service alias in the user any svc-dhcp permit rule.
Answer: D
NEW QUESTION 17
What is one reason for a network administrator to visit the Dashboard > Usage window on an Aruba Mobility Master (MM)?
- A. to check license usage and determine the need for additional licenses
- B. to analyze short terms trends in network usage by client, AP, and application
- C. to view system usage statistics for the MM and troubleshoot potential issues
- D. to generate reports about traffic patterns and network usage over the past several months
Answer: B
NEW QUESTION 18
Refer to the exhibit.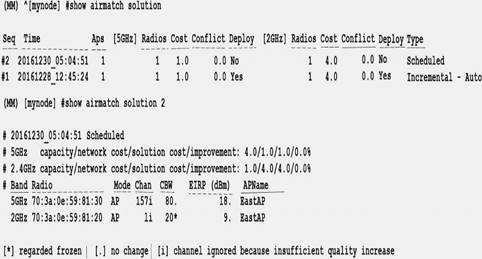
An Aruba solution uses AirMatch with the default AirMatch profile settings. A network administrator sees that a scheduled optimization was completed, but a plan was not deployed.
Based on the exhibit, why did this occur?
- A. The cost of the new plan exceeds the amount allowed by the feature license
- B. The new plan did not offer significantly improved quality
- C. The solution uses master-local mode
- D. ARM is disabled in the radio profile, so AP radios are considered frozen
Answer: B
NEW QUESTION 19
What is a requirement for the Dashboard > Traffic Analysis window on the Aruba Mobility Master (MM) to show data?
- A. Airmatch and ClientMatch must be enabled.
- B. The solution must have active PEFNG licenses.
- C. Firewall policies must include application filtering rules.
- D. WLANs must use the decrypt-tunnel forwarding option.
Answer: B
NEW QUESTION 20
What is one setting that a network administrator can configure for user roles in an Aruba solution?
- A. DHCP pool
- B. ClientMatch rules
- C. source NAT
- D. Maximum session
Answer: A
NEW QUESTION 21
Assume that administrators accept the default forwarding mode for WLANs. How does wireless user traffic flow in a master-local architecture, and how does it flow in a Mobility Master (MM) architecture?
- A. In the master-local architecture, all traffic is tunneled to the master controller to handl
- B. In a MM architecture, all traffic is tunneled to the MM to handle.
- C. In both architectures, APs forward corporate user traffic locally and tunnel guest user traffic to a Mobility Controller (MC) to handle.
- D. In both architectures, traffic is tunneled to a Mobility Controller (MC) to handle.
- E. In the master-local architecture, traffic is tunneled to a local Mobility Controller (MC) to handl
- F. In a MM architecture, all traffic is tunneled to the MM to handle.
Answer: B
NEW QUESTION 22
What is the difference between WPA and WPA2 encryption?
- A. WPA encryption uses symmetric keys, and WPA2 encryption uses asymmetric keys.
- B. WPA encryption acts at Layer 3, and WPA2 encryption acts at Layer 2.
- C. WPA encryption works only with preshared key (PSK) authentication, and WPA2 encryption works with both PSK and 802.1X.
- D. WPA encryption uses TKIP by default, and WPA2 encryption uses AES by default.
Answer: D
NEW QUESTION 23
A company wants to provide wireless access for guests with their Aruba solution. Which configuration feature requires the customer to purchase PEFNG licenses?
- A. redirection of guests to an external captive portal
- B. provision of DHCP services to unauthenticated guests
- C. addition of custom rules to control access for authenticated guests
- D. customization of the internal captive portal login page
Answer: C
NEW QUESTION 24
......
Recommend!! Get the Full HPE6-A42 dumps in VCE and PDF From DumpSolutions.com, Welcome to Download: https://www.dumpsolutions.com/HPE6-A42-dumps/ (New 122 Q&As Version)
