Master the SSCP System Security Certified Practitioner (SSCP) content and be ready for exam day success quickly with this Pass4sure SSCP practice. We guarantee it!We make it a reality and give you real SSCP questions in our ISC2 SSCP braindumps.Latest 100% VALID ISC2 SSCP Exam Questions Dumps at below page. You can use our ISC2 SSCP braindumps and pass your exam.
Free SSCP Demo Online For ISC2 Certifitcation:
NEW QUESTION 1
Which of the following is not a component of a Operations Security "triples"?
- A. Asset
- B. Threat
- C. Vulnerability
- D. Risk
Answer: D
Explanation:
The Operations Security domain is concerned with triples - threats, vulnerabilities and assets.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 216.
NEW QUESTION 2
A prolonged complete loss of electric power is a:
- A. brownout
- B. blackout
- C. surge
- D. fault
Answer: B
Explanation:
A prolonged power outage is a blackout.
From: HARRIS, Shon, All-In-One CISSP Certification Exam Guide, 3rd. Edition McGraw- Hill/Osborne, 2005, page 368.
NEW QUESTION 3
Which of the following is NOT a basic component of security architecture?
- A. Motherboard
- B. Central Processing Unit (CPU
- C. Storage Devices
- D. Peripherals (input/output devices)
Answer: A
Explanation:
The CPU, storage devices and peripherals each have specialized roles in the security archecture. The CPU, or microprocessor, is the brains behind a computer system and performs calculations as it solves problemes and performs system tasks. Storage devices provide both long- and short-term stoarge of information that the CPU has either processed or may process. Peripherals (scanners, printers, modems, etc) are devices that either input datra or receive the data output by the CPU.
The motherboard is the main circuit board of a microcomputer and contains the connectors for attaching additional boards. Typically, the motherboard contains the CPU, BIOS, memory, mass storage interfaces, serial and parallel ports, expansion slots, and all the controllers required to control standard peripheral devices.
Reference(s) used for this question:
TIPTON, Harold F., The Official (ISC)2 Guide to the CISSP CBK (2007), page 308.
NEW QUESTION 4
What is NOT true with pre shared key authentication within IKE / IPsec protocol?
- A. Pre shared key authentication is normally based on simple passwords
- B. Needs a Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) to work
- C. IKE is used to setup Security Associations
- D. IKE builds upon the Oakley protocol and the ISAKMP protocol.
Answer: B
Explanation:
Internet Key Exchange (IKE or IKEv2) is the protocol used to set up a security association (SA) in the IPsec protocol suite. IKE builds upon the Oakley protocol and ISAKMP. IKE uses X.509 certificates for authentication which are either pre-shared or distributed using DNS (preferably with DNSSEC) and a Diffie?CHellman key exchange to set up a shared session secret from which cryptographic keys are derived.
Internet Key Exchange (IKE) Internet key exchange allows communicating partners to prove their identity to each other and establish a secure communication channel, and is applied as an authentication component of IPSec.
IKE uses two phases:
Phase 1: In this phase, the partners authenticate with each other, using one of the following:
Shared Secret: A key that is exchanged by humans via telephone, fax, encrypted e-mail, etc.
Public Key Encryption: Digital certificates are exchanged.
Revised mode of Public Key Encryption: To reduce the overhead of public key encryption, a nonce (a Cryptographic function that refers to a number or bit string used only once, in security engineering) is encrypted with the communicating partner??s public key, and the peer??s identity is encrypted with symmetric encryption using the nonce as the key. Next, IKE establishes a temporary security association and secure tunnel to protect the rest of the key exchange. Phase 2: The peers?? security associations are established, using the secure tunnel and temporary SA created at the end of phase 1.
The following reference(s) were used for this question:
Hernandez CISSP, Steven (2012-12-21). Official (ISC)2 Guide to the CISSP CBK, Third Edition ((ISC)2 Press) (Kindle Locations 7032-7048). Auerbach Publications. Kindle Edition.
and
RFC 2409 at http://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc2409 and
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Internet_Key_Exchange
NEW QUESTION 5
Which of the following would be the best reason for separating the test and development environments?
- A. To restrict access to systems under test.
- B. To control the stability of the test environment.
- C. To segregate user and development staff.
- D. To secure access to systems under development.
Answer: B
Explanation:
The test environment must be controlled and stable in order to ensure that development projects are tested in a realistic environment which, as far as possible, mirrors the live environment.
Reference(s) used for this question:
Information Systems Audit and Control Association, Certified Information Systems Auditor 2002 review manual, chapter 6: Business Application System Development, Acquisition, Implementation and Maintenance (page 309).
NEW QUESTION 6
What kind of encryption is realized in the S/MIME-standard?
- A. Asymmetric encryption scheme
- B. Password based encryption scheme
- C. Public key based, hybrid encryption scheme
- D. Elliptic curve based encryption
Answer: C
Explanation:
S/MIME (for Secure MIME, or Secure Multipurpose Mail Extension) is a security process used for e-mail exchanges that makes it possible to guarantee the confidentiality and non-repudiation of electronic messages.
S/MIME is based on the MIME standard, the goal of which is to let users attach files other than ASCII text files to electronic messages. The MIME standard therefore makes it possible to attach all types of files to e-mails.
S/MIME was originally developed by the company RSA Data Security. Ratified in July 1999 by the IETF, S/MIME has become a standard, whose specifications are contained in RFCs 2630 to 2633.
How S/MIME works
The S/MIME standard is based on the principle of public-key encryption. S/MIME therefore makes it possible to encrypt the content of messages but does not encrypt the communication.
The various sections of an electronic message, encoded according to the MIME standard, are each encrypted using a session key.
The session key is inserted in each section's header, and is encrypted using the recipient's public key. Only the recipient can open the message's body, using his private key, which guarantees the confidentiality and integrity of the received message.
In addition, the message's signature is encrypted with the sender's private key. Anyone intercepting the communication can read the content of the message's signature, but this ensures the recipient of the sender's identity, since only the sender is capable of encrypting a message (with his private key) that can be decrypted with his public key.
Reference(s) used for this question: http://en.kioskea.net/contents/139-cryptography-s-mime
RFC 2630: Cryptographic Message Syntax;
OPPLIGER, Rolf, Secure Messaging with PGP and S/MIME, 2000, Artech House; HARRIS, Shon, All-In-One CISSP Certification Exam Guide, 2001, McGraw-Hill/Osborne, page 570;
SMITH, Richard E., Internet Cryptography, 1997, Addison-Wesley Pub Co.
NEW QUESTION 7
Which of the following protocols' primary function is to send messages between network devices regarding the health of the network?
- A. Reverse Address Resolution Protocol (RARP).
- B. Address Resolution Protocol (ARP).
- C. Internet Protocol (IP).
- D. Internet Control Message protocol (ICMP).
Answer: D
Explanation:
Its primary function is to send messages between network devices regarding the health of the network. ARP matches an IP address to an Ethernet address. RARP matches and Ethernet address to an IP address. ICMP runs on top of IP.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 87.
NEW QUESTION 8
Which of the following access control models requires defining classification for objects?
- A. Role-based access control
- B. Discretionary access control
- C. Identity-based access control
- D. Mandatory access control
Answer: D
Explanation:
With mandatory access control (MAC), the authorization of a subject's access to an object is dependant upon labels, which indicate the subject's clearance, and classification of objects.
The Following answers were incorrect:
Identity-based Access Control is a type of Discretionary Access Control (DAC), they are synonymous.
Role Based Access Control (RBAC) and Rule Based Access Control (RuBAC or RBAC) are types of Non Discretionary Access Control (NDAC).
Tip:
When you have two answers that are synonymous they are not the right choice for sure.
There is only one access control model that makes use of Label, Clearances, and Categories, it is Mandatory Access Control, none of the other one makes use of those items.
Reference(s) used for this question:
KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, Chapter 2: Access control systems (page 33).
NEW QUESTION 9
What is called a sequence of characters that is usually longer than the allotted number for a password?
- A. passphrase
- B. cognitive phrase
- C. anticipated phrase
- D. Real phrase
Answer: A
Explanation:
A passphrase is a sequence of characters that is usually longer than the allotted number for a password.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, page 37.
NEW QUESTION 10
What best describes a scenario when an employee has been shaving off pennies from multiple accounts and depositing the funds into his own bank account?
- A. Data fiddling
- B. Data diddling
- C. Salami techniques
- D. Trojan horses
Answer: C
Explanation:
Source: HARRIS, Shon, All-In-One CISSP Certification Exam Guide, McGraw-Hill/Osborne, 2001, Page 644.
NEW QUESTION 11
Which of the following best allows risk management results to be used knowledgeably?
- A. A vulnerability analysis
- B. A likelihood assessment
- C. An uncertainty analysis
- D. A threat identification
Answer: C
Explanation:
Risk management consists of two primary and one underlying activity; risk assessment and risk mitigation are the primary activities and uncertainty analysis is the underlying one. After having performed risk assessment and mitigation, an uncertainty analysis should be performed. Risk management must often rely on speculation, best guesses, incomplete data, and many unproven assumptions. A documented uncertainty analysis allows the risk management results to be used knowledgeably. A vulnerability analysis, likelihood assessment and threat identification are all parts of the collection and analysis of data part of the risk assessment, one of the primary activities of risk management.
Source: SWANSON, Marianne & GUTTMAN, Barbara, National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), NIST Special Publication 800-14, Generally Accepted Principles and Practices for Securing Information Technology Systems, September 1996 (pages 19-21).
NEW QUESTION 12
Which of the following best corresponds to the type of memory addressing where the address location that is specified in the program instruction contains the address of the final desired location?
- A. Direct addressing
- B. Indirect addressing
- C. Indexed addressing
- D. Program addressing
Answer: B
Explanation:
Indirect addressing is when the address location that is specified in the program instruction contains the address of the final desired location. Direct addressing is
when a portion of primary memory is accessed by specifying the actual address of the memory location. Indexed addressing is when the contents of the address defined in the program's instruction is added to that of an index register. Program addressing is not a defined memory addressing mode.
Source: WALLHOFF, John, CBK#6 Security Architecture and Models (CISSP Study Guide), April 2002 (page 2).
NEW QUESTION 13
Which type of attack involves the alteration of a packet at the IP level to convince a system that it is communicating with a known entity in order to gain access to a system?
- A. TCP sequence number attack
- B. IP spoofing attack
- C. Piggybacking attack
- D. Teardrop attack
Answer: B
Explanation:
An IP spoofing attack is used to convince a system that it is communication with a known entity that gives an intruder access. It involves modifying the source address of a packet for a trusted source's address. A TCP sequence number attack involves hijacking a session between a host and a target by predicting the target's choice of an
initial TCP sequence number. Piggybacking refers to an attacker gaining unauthorized access to a system by using a legitimate user's connection. A teardrop attack consists of modifying the length and fragmentation offset fields in sequential IP packets so the target system becomes confused and crashes after it receives contradictory instructions on how the fragments are offset on these packets.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, Chapter 3: Telecommunications and Network Security (page 77).
NEW QUESTION 14
Which of the following usually provides reliable, real-time information without consuming network or host resources?
- A. network-based IDS
- B. host-based IDS
- C. application-based IDS
- D. firewall-based IDS
Answer: A
Explanation:
A network-based IDS usually provides reliable, real-time information without consuming network or host resources.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the
Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 48.
NEW QUESTION 15
Which of the following would best describe a Concealment cipher?
- A. Permutation is used, meaning that letters are scrambled.
- B. Every X number of words within a text, is a part of the real message.
- C. Replaces bits, characters, or blocks of characters with different bits, characters or blocks.
- D. Hiding data in another message so that the very existence of the data is concealed.
Answer: B
Explanation:
When a concealment cipher is used, every X number of words within a text, is a part of the real message. The message is within another message.
A concealment cipher is a message within a message. If my other super-secret spy buddy and I decide our key value is every third word, then when I get a message from him, I will pick out every third word and write it down. Suppose he sends me a message that reads, ??The saying, ??The time is right?? is not cow language, so is now a dead subject.?? Because my key is every third word, I come up with ??The right cow is dead.?? This again means nothing to me, and I am now turning in my decoder ring.
Concealment ciphers include the plaintext within the ciphertext. It is up to the recipient to know which letters or symbols to exclude from the ciphertext in order to yield the plaintext. Here is an example of a concealment cipher:
i2l32i5321k34e1245ch456oc12ol234at567e
Remove all the numbers, and you'll have i like chocolate. How about this one? Larry even appears very excited. No one worries.
The first letter from each word reveals the message leave now. Both are easy, indeed, but many people have crafted more ingenious ways of concealing the messages. By the way, this type of cipher doesn't even need ciphertext, such as that in the above examples.
Consider the invisible drying ink that kids use to send secret messages. In a more extreme example, a man named Histiaeus, during 5th century B.C., shaved the head of a trusted slave, then tattooed the message onto his bald head. When the slave's hair grew back, Histiaeus sent the slave to the message's intended recipient, Aristagoros, who shaved the slave's head and read the message instructing him to revolt.
The following answers are incorrect:
A transposition cipher uses permutations.
A substitution cipher replaces bits, characters, or blocks of characters with different bits, characters or blocks.
Steganography refers to hiding the very existence of the message.
Source: WALLHOFF, John, CBK#5 Cryptography (CISSP Study Guide), April 2002 (page 1).
and also see: http://www.go4expert.com/forums/showthread.php?t=415
NEW QUESTION 16
An effective information security policy should not have which of the following characteristic?
- A. Include separation of duties
- B. Be designed with a short- to mid-term focus
- C. Be understandable and supported by all stakeholders
- D. Specify areas of responsibility and authority
Answer: B
Explanation:
An effective information security policy should be designed with a long-term focus. All other characteristics apply.
Source: ALLEN, Julia H., The CERT Guide to System and Network Security Practices, Addison-Wesley, 2001, Appendix B, Practice-Level Policy Considerations (page 397).
NEW QUESTION 17
Which of the following services is NOT provided by the digital signature standard (DSS)?
- A. Encryption
- B. Integrity
- C. Digital signature
- D. Authentication
Answer: A
Explanation:
DSS provides Integrity, digital signature and Authentication, but does not provide Encryption.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, Chapter 4: Cryptography (page 160).
NEW QUESTION 18
How many rounds are used by DES?
- A. 16
- B. 32
- C. 64
- D. 48
Answer: A
Explanation:
DES is a block encryption algorithm using 56-bit keys and 64-bit blocks that are divided in half and each character is encrypted one at a time. The characters are put through 16 rounds of transposition and substitution functions. Triple DES uses 48 rounds. Source: WALLHOFF, John, CBK#5 Cryptography (CISSP Study Guide), April 2002 (page 3).
NEW QUESTION 19
Access Control techniques do not include which of the following choices?
- A. Relevant Access Controls
- B. Discretionary Access Control
- C. Mandatory Access Control
- D. Lattice Based Access Control
Answer: A
Explanation:
Access Control Techniques Discretionary Access Control
Mandatory Access Control Lattice Based Access Control Rule-Based Access Control Role-Based Access Control
Source: DUPUIS, Clement, Access Control Systems and Methodology, Version 1, May 2002, CISSP Open Study Group Study Guide for Domain 1, Page 13.
NEW QUESTION 20
Which of the following item would best help an organization to gain a common understanding of functions that are critical to its survival?
- A. A risk assessment
- B. A business assessment
- C. A disaster recovery plan
- D. A business impact analysis
Answer: D
Explanation:
A Business Impact Analysis (BIA) is an assessment of an organization's business functions to develop an understanding of their criticality, recovery time objectives, and resources needed.
By going through a Business Impact Analysis, the organization will gain a common understanding of functions that are critical to its survival.
A risk assessment is an evaluation of the exposures present in an organization's external and internal environments.
A Business Assessment generally include Business Analysis as a discipline and it has heavy overlap with requirements analysis sometimes also called requirements engineering, but focuses on identifying the changes to an organization that are required for it to achieve strategic goals. These changes include changes to strategies, structures, policies, processes, and information systems.
A disaster recovery plan is the comprehensive statement of consistent actions to be taken before, during and after a disruptive event that causes a significant loss of information systems resources.
Source: BARNES, James C. & ROTHSTEIN, Philip J., A Guide to Business Continuity Planning, John Wiley & Sons, 2001 (page 57).
NEW QUESTION 21
Which of the following is an IP address that is private (i.e. reserved for internal networks, and not a valid address to use on the Internet)?
- A. 192.168.42.5
- B. 192.166.42.5
- C. 192.175.42.5
- D. 192.1.42.5
Answer: A
Explanation:
This is a valid Class C reserved address. For Class C, the reserved addresses are 192.168.0.0 - 192.168.255.255.
The private IP address ranges are defined within RFC 1918: RFC 1918 private ip address range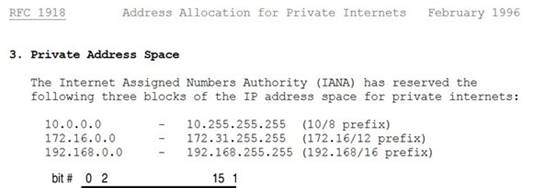
C:\Users\MCS\Desktop\1.jpg
The following answers are incorrect:
192.166.42.5 Is incorrect because it is not a Class C reserved address. 192.175.42.5 Is incorrect because it is not a Class C reserved address.
192.1.42.5 Is incorrect because it is not a Class C reserved address.
NEW QUESTION 22
Which type of password provides maximum security because a new password is required for each new log-on?
- A. One-time or dynamic password
- B. Congnitive password
- C. Static password
- D. Passphrase
Answer: A
Explanation:
"one-time password" provides maximum security because a new password is required for each new log-on.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 36.
NEW QUESTION 23
Which of the following monitors network traffic in real time?
- A. network-based IDS
- B. host-based IDS
- C. application-based IDS
- D. firewall-based IDS
Answer: A
Explanation:
This type of IDS is called a network-based IDS because monitors network traffic in real time.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 48.
NEW QUESTION 24
Qualitative loss resulting from the business interruption does NOT usually include:
- A. Loss of revenue
- B. Loss of competitive advantage or market share
- C. Loss of public confidence and credibility
- D. Loss of market leadership
Answer: A
Explanation:
This question is testing your ability to evaluate whether items on the list are Qualitative or Quantitative. All of the items listed were Qualitative except Lost of Revenue which is Quantitative.
Those are mainly two approaches to risk analysis, see a description of each below:
A quantitative risk analysis is used to assign monetary and numeric values to all elements of the risk analysis process. Each element within the analysis (asset value, threat frequency, severity of vulnerability, impact damage, safeguard costs, safeguard effectiveness, uncertainty, and probability items) is quantified and entered into equations to determine total and residual risks. It is more of a scientific or mathematical approach to risk analysis compared to qualitative.
A qualitative risk analysis uses a ??softer?? approach to the data elements of a risk analysis . It does not quantify that data, which means that it does not assign numeric values to the data so that they can be used in equations.
Qualitative and quantitative impact information should be gathered and then properly analyzed and interpreted. The goal is to see exactly how a business will be affected by different threats.
The effects can be economical, operational, or both. Upon completion of the data analysis, it should be reviewed with the most knowledgeable people within the company to ensure that the findings are appropriate and that it describes the real risks and impacts the organization faces. This will help flush out any additional data points not originally obtained and will give a fuller understanding of all the possible business impacts.
Loss criteria must be applied to the individual threats that were identified. The criteria may include the following:
Loss in reputation and public confidence Loss of competitive advantages Increase in operational expenses Violations of contract agreements
Violations of legal and regulatory requirements
Delayed income costs Loss in revenue
Loss in productivity
Reference used for this question:
Harris, Shon (2012-10-18). CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, 6th Edition (p. 909). McGraw- Hill. Kindle Edition.
NEW QUESTION 25
Risk reduction in a system development life-cycle should be applied:
- A. Mostly to the initiation phase.
- B. Mostly to the development phase.
- C. Mostly to the disposal phase.
- D. Equally to all phases.
Answer: D
Explanation:
Risk is defined as the combination of the probability that a particular threat source will exploit, or trigger, a particular information system vulnerability and the resulting mission impact should this occur. Previously, risk avoidance was a common IT security goal. That changed as the nature of the risk became better understood. Today, it is recognized that elimination of all risk is not cost-effective. A cost-benefit analysis should be conducted for each proposed control. In some cases, the benefits of a more secure system may not justify the direct and indirect costs. Benefits include more than just prevention of monetary loss; for example, controls may be essential for maintaining public trust and confidence. Direct costs include the cost of purchasing and installing a given technology; indirect costs include decreased system performance and additional training. The goal is to enhance mission/business capabilities by managing mission/business risk to an acceptable level.
Source: STONEBURNER, Gary & al, National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), NIST Special Publication 800-27, Engineering Principles for Information Technology Security (A Baseline for Achieving Security), June 2001 (page 8).
NEW QUESTION 26
......
100% Valid and Newest Version SSCP Questions & Answers shared by Downloadfreepdf.net, Get Full Dumps HERE: https://www.downloadfreepdf.net/SSCP-pdf-download.html (New 1074 Q&As)
