It is impossible to pass ISC2 SSCP exam without any help in the short term. Come to Passleader soon and find the most advanced, correct and guaranteed ISC2 SSCP practice questions. You will get a surprising result by our Up to date System Security Certified Practitioner (SSCP) practice guides.
Online SSCP free questions and answers of New Version:
NEW QUESTION 1
Which of the following can be used as a covert channel?
- A. Storage and timing.
- B. Storage and low bits.
- C. Storage and permissions.
- D. Storage and classification.
Answer: A
Explanation:
The Orange book requires protection against two types of covert channels, Timing and Storage.
The following answers are incorrect:
Storage and low bits. Is incorrect because, low bits would not be considered a covert channel.
Storage and permissions. Is incorrect because, permissions would not be considered a covert channel.
Storage and classification. Is incorrect because, classification would not be considered a covert channel.
NEW QUESTION 2
The Diffie-Hellman algorithm is primarily used to provide which of the following?
- A. Confidentiality
- B. Key Agreement
- C. Integrity
- D. Non-repudiation
Answer: B
Explanation:
Diffie and Hellman describe a means for two parties to agree upon a shared secret in such a way that the secret will be unavailable to eavesdroppers. This secret may then be converted into cryptographic keying material for other (symmetric) algorithms. A large number of minor variants of this process exist. See RFC 2631 Diffie-Hellman Key Agreement Method for more details.
In 1976, Diffie and Hellman were the first to introduce the notion of public key cryptography, requiring a system allowing the exchange of secret keys over non-secure channels. The Diffie-Hellman algorithm is used for key exchange between two parties communicating with each other, it cannot be used for encrypting and decrypting messages, or digital signature. Diffie and Hellman sought to address the issue of having to exchange keys via courier and other unsecure means. Their efforts were the FIRST asymmetric key agreement algorithm. Since the Diffie-Hellman algorithm cannot be used for encrypting and decrypting it cannot provide confidentiality nor integrity. This algorithm also does not provide for digital signature functionality and thus non-repudiation is not a choice.
NOTE: The DH algorithm is susceptible to man-in-the-middle attacks. KEY AGREEMENT VERSUS KEY EXCHANGE
A key exchange can be done multiple way. It can be done in person, I can generate a key
and then encrypt the key to get it securely to you by encrypting it with your public key. A Key Agreement protocol is done over a public medium such as the internet using a mathematical formula to come out with a common value on both sides of the communication link, without the ennemy being able to know what the common agreement is.
The following answers were incorrect:
All of the other choices were not correct choices Reference(s) used for this question:
Shon Harris, CISSP All In One (AIO), 6th edition . Chapter 7, Cryptography, Page 812. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Diffie%E2%80%93Hellman_key_exchange http://www.google.com/patents?vid=4200770
NEW QUESTION 3
Which of the following is NOT an advantage that TACACS+ has over TACACS?
- A. Event logging
- B. Use of two-factor password authentication
- C. User has the ability to change his password
- D. Ability for security tokens to be resynchronized
Answer: A
Explanation:
Although TACACS+ provides better audit trails, event logging is a service that is provided with TACACS.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, Chapter 3: Telecommunications and Network Security (page 121).
NEW QUESTION 4
Which of the following questions is less likely to help in assessing physical access controls?
- A. Does management regularly review the list of persons with physical access to sensitive facilities?
- B. Is the operating system configured to prevent circumvention of the security software and application controls?
- C. Are keys or other access devices needed to enter the computer room and media library?
- D. Are visitors to sensitive areas signed in and escorted?
Answer: B
Explanation:
Physical security and environmental security are part of operational controls, and are measures taken to protect systems, buildings, and related supporting infrastructures against threats associated with their physical environment. All the questions above are useful in assessing physical access controls except for the one regarding operating system configuration, which is a logical access control.
Source: SWANSON, Marianne, NIST Special Publication 800-26, Security Self- Assessment Guide for Information Technology Systems, November 2001 (Pages A-21 to A-24).
NEW QUESTION 5
Which of the following assertions is NOT true about pattern matching and anomaly detection in intrusion detection?
- A. Anomaly detection tends to produce more data
- B. A pattern matching IDS can only identify known attacks
- C. Stateful matching scans for attack signatures by analyzing individual packets instead of traffic streams
- D. An anomaly-based engine develops baselines of normal traffic activity and throughput, and alerts on deviations from these baselines
Answer: C
Explanation:
This is wrong which makes this the correct choice. This statement is not true as stateful matching scans for attack signatures by analyzing traffic streams rather than individual packets. Stateful matching intrusion detection takes pattern matching to the next level.
As networks become faster there is an emerging need for security analysis techniques that can keep up with the increased network throughput. Existing network-based intrusion detection sensors can barely keep up with bandwidths of a few hundred Mbps. Analysis tools that can deal with higher throughput are unable to maintain state between different steps of an attack or they are limited to the analysis of packet headers.
The following answers are all incorrect:
Anomaly detection tends to produce more data is true as an anomaly-based IDS produces a lot of data as any activity outside of expected behavior is recorded.
A pattern matching IDS can only identify known attacks is true as a pattern matching IDS works by comparing traffic streams against signatures. These signatures are created for known attacks.
An anomaly-based engine develops baselines of normal traffic activity and throughput, and alerts on deviations from these baselines is true as the assertion is a characteristic of a statistical anomaly-based IDS.
Reference:
Official guide to the CISSP CBK. Pages 198 to 201 http://cs.ucsb.edu/~vigna/publications/2003_vigna_robertson_kher_kemmerer_ACSAC03.p
df
NEW QUESTION 6
What is called an attack in which an attacker floods a system with connection requests but does not respond when the target system replies to those requests?
- A. Ping of death attack
- B. SYN attack
- C. Smurf attack
- D. Buffer overflow attack
Answer: B
Explanation:
A SYN attack occurs when an attacker floods the target system's small "in- process" queue with connection requests, but it does not respond when the target system replies to those requests. This causes the target system to "time out" while waiting for the proper response, which makes the system crash or become unusable. A buffer overflow attack occurs when a process receives much more data than expected. One common buffer overflow attack is the ping of death, where an attacker sends IP packets that exceed the maximum legal length (65535 octets). A smurf attack is an attack where the attacker spoofs the source IP address in an ICMP ECHO broadcast packet so it seems to have originated at the victim's system, in order to flood it with REPLY packets.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, Chapter 3: Telecommunications and Network Security (page 76).
NEW QUESTION 7
What is the 802.11 standard related to?
- A. Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)
- B. Wireless network communications
- C. Packet-switching technology
- D. The OSI/ISO model
Answer: B
Explanation:
The 802.11 standard outlines how wireless clients and APs communicate, lays out the specifications of their interfaces, dictates how signal transmission should take place, and describes how authentication, association, and security should be implemeted.
The following answers are incorrect:
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) Public Key Infrastructure is a supporting infrastructure to manage public keys. It is not part of the IEEE 802 Working Group standard.
Packet-switching technology A packet-switching technology is not included in the IEEE 802 Working Group standard. It is a technology where-in messages are broken up into packets,
which then travel along different routes to the destination.
The OSI/ISO model The Open System Interconnect model is a sevel-layer model defined as an international standard describing network communications.
The following reference(s) were/was used to create this question:
Source: Shon Harris - "All-in-One CISSP Exam Guide" Fourth Edition; Chapter 7 - Telecommunications and Network Security: pg. 624.
802.11 refers to a family of specifications developed by the IEEE for Wireless LAN technology. 802.11 specifies an over-the-air interface between a wireless client and a base station or between two wireless clients. The IEEE accepted the specification in 1997. There are several specifications in the 802.11 family:
802.11 # applies to wireless LANs and provides 1 or 2 Mbps transmission in the 2.4 GHz band using either frequency hopping spread spectrum (FHSS) or direct sequence spread spectrum (DSSS).
802.11a # an extension to 802.11 that applies to wireless LANs and provides up to 54 Mbps in the 5GHz band. 802.11a uses an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing encoding scheme rather than FHSS or DSSS.
802.11b (also referred to as 802.11 High Rate or Wi-Fi) # an extension to 802.11 that applies to wireless LANS and provides 11 Mbps transmission (with a fallback to 5.5, 2 and 1 Mbps) in the 2.4 GHz band. 802.11b uses only DSSS. 802.11b was a 1999 ratification to the original 802.11 standard, allowing wireless functionality comparable to Ethernet. 802.11g # applies to wireless LANs and provides 20+ Mbps in the 2.4 GHz band.
Source: 802.11 Planet's web site.
NEW QUESTION 8
Which of the following Operation Security controls is intended to prevent unauthorized intruders from internally or externally accessing the system, and to lower the amount and impact of unintentional errors that are entering the system?
- A. Detective Controls
- B. Preventative Controls
- C. Corrective Controls
- D. Directive Controls
Answer: B
Explanation:
In the Operations Security domain, Preventative Controls are designed to prevent unauthorized intruders from internally or externally accessing the system, and to lower the amount and impact of unintentional errors that are entering the system. Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 217.
NEW QUESTION 9
Attributable data should be:
- A. always traced to individuals responsible for observing and recording the data
- B. sometimes traced to individuals responsible for observing and recording the data
- C. never traced to individuals responsible for observing and recording the data
- D. often traced to individuals responsible for observing and recording the data
Answer: A
Explanation:
As per FDA data should be attributable, original, accurate, contemporaneous
and legible. In an automated system attributability could be achieved by a computer system designed to identify individuals responsible for any input.
Source: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Food and Drug Administration, Guidance for Industry - Computerized Systems Used in Clinical Trials, April 1999, page 1.
NEW QUESTION 10
Which of the following is implemented through scripts or smart agents that replays the users multiple log-ins against authentication servers to verify a user's identity which permit access to system services?
- A. Single Sign-On
- B. Dynamic Sign-On
- C. Smart cards
- D. Kerberos
Answer: A
Explanation:
SSO can be implemented by using scripts that replay the users multiple log- ins against authentication servers to verify a user's identity and to permit access to system services.
Single Sign on was the best answer in this case because it would include Kerberos. When you have two good answers within the 4 choices presented you must select the
BEST one. The high level choice is always the best. When one choice would include the
other one that would be the best as well.
Reference(s) used for this question:
KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 40.
NEW QUESTION 11
Which of the following is immune to the effects of electromagnetic interference (EMI) and therefore has a much longer effective usable length?
- A. Fiber Optic cable
- B. Coaxial cable
- C. Twisted Pair cable
- D. Axial cable
Answer: A
Explanation:
Fiber Optic cable is immune to the effects of electromagnetic interference
(EMI) and therefore has a much longer effective usable length (up to two kilometers in some cases).
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 72.
NEW QUESTION 12
Complete the blanks. When using PKI, I digitally sign a message using my key. The recipient verifies my signature using my key.
- A. Private / Public
- B. Public / Private
- C. Symmetric / Asymmetric
- D. Private / Symmetric
Answer: A
Explanation:
When we encrypt messages using our private keys which are only available to us. The person who wants to read and decrypt the message need only have our public keys to do so.
The whole point to PKI is to assure message integrity, authentication of the source, and to provide secrecy with the digital encryption.
See below a nice walktrough of Digital Signature creation and verification from the Comodo web site:
Digital Signatures apply the same functionality to an e-mail message or data file that a handwritten signature does for a paper-based document. The Digital Signature vouches for the origin and integrity of a message, document or other data file.
How do we create a Digital Signature?
The creation of a Digital Signature is a complex mathematical process. However as the complexities of the process are computed by the computer, applying a Digital Signature is no more difficult that creating a handwritten one!
The following text illustrates in general terms the processes behind the generation of a Digital Signature:
1. Alice clicks 'sign' in her email application or selects which file is to be signed.
2. Alice's computer calculates the 'hash' (the message is applied to a publicly known mathematical hashing function that coverts the message into a long number referred to as the hash).
3. The hash is encrypted with Alice's Private Key (in this case it is known as the Signing Key) to create the Digital Signature.
4. The original message and its Digital Signature are transmitted to Bob.
5. Bob receives the signed message. It is identified as being signed, so his email application knows which actions need to be performed to verify it.
6. Bob's computer decrypts the Digital Signature using Alice's Public Key.
7. Bob's computer also calculates the hash of the original message (remember - the mathematical function used by Alice to do this is publicly known).
8. Bob's computer compares the hashes it has computed from the received message with the now decrypted hash received with Alice's message.
digital signature creation and verification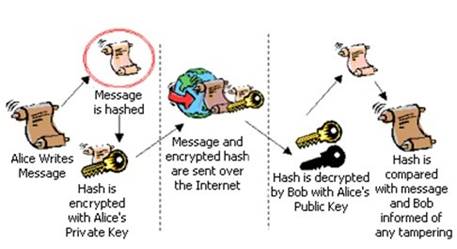
C:\Users\MCS\Desktop\1.jpg
If the message has remained integral during its transit (i.e. it has not been tampered with), when compared the two hashes will be identical.
However, if the two hashes differ when compared then the integrity of the original message has been compromised. If the original message is tampered with it will result in Bob's
computer calculating a different hash value. If a different hash value is created, then the original message will have been altered. As a result the verification of the Digital Signature will fail and Bob will be informed.
Origin, Integrity, Non-Repudiation, and Preventing Men-In-The-Middle (MITM) attacks
Eve, who wants to impersonate Alice, cannot generate the same signature as Alice because she does not have Alice's Private Key (needed to sign the message digest). If instead, Eve decides to alter the content of the message while in transit, the tampered message will create a different message digest to the original message, and Bob's computer will be able to detect that. Additionally, Alice cannot deny sending the message as it has been signed using her Private Key, thus ensuring non-repudiation.
creating and validating a digital signature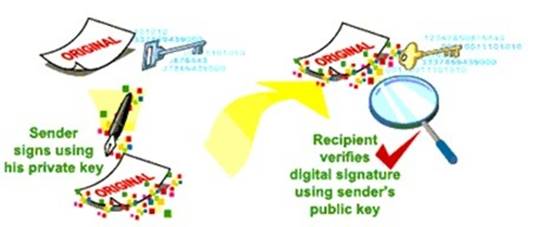
C:\Users\MCS\Desktop\1.jpg
Due to the recent Global adoption of Digital Signature law, Alice may now sign a transaction, message or piece of digital data, and so long as it is verified successfully it is a legally permissible means of proof that Alice has made the transaction or written the message.
The following answers are incorrect:
- Public / Private: This is the opposite of the right answer.
- Symmetric / Asymmetric: Not quite. Sorry. This form of crypto is asymmetric so you were almost on target.
- Private / Symmetric: Well, you got half of it right but Symmetric is wrong.
The following reference(s) was used to create this question:
The CCCure Holistic Security+ CBT, you can subscribe at: http://www.cccure.tv and
http://www.comodo.com/resources/small-business/digital-certificates3.php
NEW QUESTION 13
Which of the following protocols suite does the Internet use?
- A. IP/UDP/TCP
- B. IP/UDP/ICMP/TCP
- C. TCP/IP
- D. IMAP/SMTP/POP3
Answer: C
Explanation:
Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) is the common name for the suite of protocols that was developed by the Department of Defense (DoD) in the 1970's to support the construction of the internet. The Internet is based on TCP/IP.
The Internet protocol suite is the networking model and a set of communications protocols used for the Internet and similar networks. It is commonly known as TCP/IP, because its most important protocols, the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and the Internet Protocol (IP), were the first networking protocols defined in this standard. It is occasionally known as the DoD model, because the development of the networking model was funded by DARPA, an agency of the United States Department of Defense.
TCP/IP provides end-to-end connectivity specifying how data should be formatted, addressed, transmitted, routed and received at the destination. This functionality has been organized into four abstraction layers within the DoD Model which are used to sort all related protocols according to the scope of networking involved.
From lowest to highest, the layers are:
The link layer, containing communication technologies for a single network segment (link), The internet layer, connecting independent networks, thus establishing internetworking,
The transport layer handling process-to-process communication,
The application layer, which interfaces to the user and provides support services.
The TCP/IP model and related protocols are maintained by the Internet Engineering Task
Force (IETF).
The following answers are incorrect:
IP/UDP/TCP. This is incorrect, all three are popular protocol and they are not considered a suite of protocols.
IP/UDP/ICMP/TCP. This is incorrect, all 4 are some of the MOST commonly used protocol but they are not called a suite of protocol.
IMAP/SMTP/POP3 . This is incorrect because they are all email protocol and consist of only a few of the protocol that would be included in the TCP/IP suite of protocol.
Reference(s) used for this question:
Hernandez CISSP, Steven (2012-12-21). Official (ISC)2 Guide to the CISSP CBK, Third Edition ((ISC)2 Press) (Kindle Locations 5267-5268). Auerbach Publications. Kindle Edition.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Internet_protocol_suite
NEW QUESTION 14
A prolonged high voltage is a:
- A. spike
- B. blackout
- C. surge
- D. fault
Answer: C
Explanation:
A prolonged high voltage is a surge.
From: HARRIS, Shon, All-In-One CISSP Certification Exam Guide, 3rd. Edition McGraw- Hill/Osborne, 2005, page 368.
NEW QUESTION 15
Which xDSL flavour, appropriate for home or small offices, delivers more bandwidth downstream than upstream and over longer distance?
- A. VDSL
- B. SDSL
- C. ADSL
- D. HDSL
Answer: C
Explanation:
Asymmetric digital subscriber line (ADSL) is designed to provide more bandwidth downstream (1 to 8 Mbps) than upstream (16 to 800Kb).
DSL (Digital Subscriber Line) is a modem technology for broadband data access over
ordinary copper telephone lines (POTS) from homes and businesses. xDSL refers collectively to all types of DSL, such as ADSL (and G.Lite), HDSL, SDSL, IDSL and VDSL etc. They are sometimes referred to as last-mile (or first mile) technologies because they are used only for connections from a telephone switching station to a home or office, not between switching stations.
xDSL is similar to ISDN in as much as both operate over existing copper telephone lines (POTS) using sophisticated modulation schemes and both require the short runs to a central telephone office
Graphic below from: http://computer.howstuffworks.com/vdsl3.htm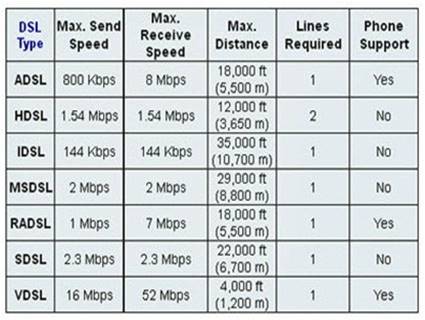
C:\Users\MCS\Desktop\1.jpg DSL speed chart
The following are incorrect answers:
Single-line Digital Subscriber Line (SDSL) deliver 2.3 Mbps of bandwidth each way. High-rate Digital Subscriber Line (HDSL) deliver 1.544 Mbps of bandwidth each way.
Very-high data-rate Digital Subscriber Line (VDSL) can deliver up to 52 Mbps downstream
over a single copper twisted pair over a relatively short distance (1000 to 4500 feet). Reference used for this question:
http://computer.howstuffworks.com/vdsl3.htm and http://www.javvin.com/protocolxDSL.html and
KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, Chapter 3: Telecommunications and Network Security (page 115).
NEW QUESTION 16
What is called the verification that the user's claimed identity is valid and is usually implemented through a user password at log-on time?
- A. Authentication
- B. Identification
- C. Integrity
- D. Confidentiality
Answer: A
Explanation:
Authentication is verification that the user's claimed identity is valid and is usually implemented through a user password at log-on time.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 36.
NEW QUESTION 17
Which of the following is NOT a correct notation for an IPv6 address?
- A. 2001:0db8:0:0:0:0:1428:57ab
- B. ABCD:EF01:2345:6789:ABCD:EF01:2345:6789
- C. ::1
- D. 2001:DB8::8:800::417A
Answer: D
Explanation:
This is not a correct notation for an IPv6 address because the the "::" can only appear once in an address. The use of "::" is a shortcut notation that indicates one or more groups of 16 bits of zeros.
1 is the loopback address using the special notation Reference: IP Version 6 Addressing Architecture
http://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc4291#section-2.1
NEW QUESTION 18
Identification and authentication are the keystones of most access control systems. Identification establishes:
- A. User accountability for the actions on the system.
- B. Top management accountability for the actions on the system.
- C. EDP department accountability for the actions of users on the system.
- D. Authentication for actions on the system
Answer: A
Explanation:
Identification and authentication are the keystones of most access control systems. Identification establishes user accountability for the actions on the system.
The control environment can be established to log activity regarding the identification, authentication, authorization, and use of privileges on a system. This can be used to detect the occurrence of errors, the attempts to perform an unauthorized action, or to validate when provided credentials were exercised. The logging system as a detective device provides evidence of actions (both successful and unsuccessful) and tasks that were executed by authorized users.
Once a person has been identified through the user ID or a similar value, she must be authenticated, which means she must prove she is who she says she is. Three general factors can be used for authentication: something a person knows, something a person has, and something a person is. They are also commonly called authentication by knowledge, authentication by ownership, and authentication by characteristic.
For a user to be able to access a resource, he first must prove he is who he claims to be, has the necessary credentials, and has been given the necessary rights or privileges to perform the actions he is requesting. Once these steps are completed successfully, the user can access and use network resources; however, it is necessary to track the user??s activities and enforce accountability for his actions.
Identification describes a method of ensuring that a subject (user, program, or process) is the entity it claims to be. Identification can be provided with the use of a username or account number. To be properly authenticated, the subject is usually required to provide a second piece to the credential set. This piece could be a password, passphrase,
cryptographic key, personal identification number (PIN), anatomical attribute, or token.
These two credential items are compared to information that has been previously stored for this subject. If these credentials match the stored information, the subject is authenticated. But we are not done yet. Once the subject provides its credentials and is properly identified, the system it is trying to access needs to determine if this subject has been given the necessary rights and privileges to carry out the requested actions. The system will look at some type of access control matrix or compare security labels to verify that this subject may indeed access the requested resource and perform the actions it is attempting. If the system determines that the subject may access the resource, it authorizes the subject.
Although identification, authentication, authorization, and accountability have close and complementary definitions, each has distinct functions that fulfill a specific requirement in the process of access control. A user may be properly identified and authenticated to the network, but he may not have the authorization to access the files on the file server. On the other hand, a user may be authorized to access the files on the file server, but until she is properly identified and authenticated, those resources are out of reach.
Reference(s) used for this question:
Schneiter, Andrew (2013-04-15). Official (ISC)2 Guide to the CISSP CBK, Third Edition: Access Control ((ISC)2 Press) (Kindle Locations 889-892). Auerbach Publications. Kindle Edition.
and
Harris, Shon (2012-10-25). CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, 6th Edition (Kindle Locations 3875-3878). McGraw-Hill. Kindle Edition.
and
Harris, Shon (2012-10-25). CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, 6th Edition (Kindle Locations 3833-3848). McGraw-Hill. Kindle Edition.
and
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 36.
NEW QUESTION 19
Which of the following would be the MOST serious risk where a systems development life cycle methodology is inadequate?
- A. The project will be completed late.
- B. The project will exceed the cost estimates.
- C. The project will be incompatible with existing systems.
- D. The project will fail to meet business and user needs.
Answer: D
Explanation:
This is the most serious risk of inadequate systems development life cycle methodolgy.
The following answers are incorrect because :
The project will be completed late is incorrect as it is not most devastating as the above answer.
The project will exceed the cost estimates is also incorrect when compared to the above correct answer.
The project will be incompatible with existing systems is also incorrect when compared to the above correct answer.
Reference: Information Systems Audit and Control Association, Certified Information Systems Auditor 2002 review manual, chapter 6: Business Application System Development, Acquisition, Implementation and Maintenance (page 290).
NEW QUESTION 20
A department manager has read access to the salaries of the employees in his/her department but not to the salaries of employees in other departments. A database security mechanism that enforces this policy would typically be said to provide which of the following?
- A. Content-dependent access control
- B. Context-dependent access control
- C. Least privileges access control
- D. Ownership-based access control
Answer: A
Explanation:
When access control is based on the content of an object, it is considered to be content dependent access control.
Content-dependent access control is based on the content itself. The following answers are incorrect:
context-dependent access control. Is incorrect because this type of control is based on what the context is, facts about the data rather than what the object contains.
least privileges access control. Is incorrect because this is based on the least amount of rights needed to perform their jobs and not based on what is contained in the database. ownership-based access control. Is incorrect because this is based on the owner of the data and and not based on what is contained in the database.
References:
OIG CBK Access Control (page 191)
NEW QUESTION 21
If an employee's computer has been used by a fraudulent employee to commit a crime, the hard disk may be seized as evidence and once the investigation is complete it would follow the normal steps of the Evidence Life Cycle. In such case, the Evidence life cycle would not include which of the following steps listed below?
- A. Acquisition collection and identification
- B. Analysis
- C. Storage, preservation, and transportation
- D. Destruction
Answer: D
Explanation:
Unless the evidence is illegal then it should be returned to owner, not destroyed.
The Evidence Life Cycle starts with the discovery and collection of the evidence. It progresses through the following series of states until it is finally returned to the victim or owner:
• Acquisition collection and identification
• Analysis
• Storage, preservation, and transportation
• Presented in court
• Returned to victim (owner)
The Second edition of the ISC2 book says on page 529-530:
Identifying evidence: Correctly identifying the crime scene, evidence, and potential containers of evidence.
Collecting or acquiring evidence: Adhering to the criminalistic principles and ensuring that the contamination and the destruction of the scene are kept to a minimum. Using sound, repeatable, collection techniques that allow for the demonstration of the accuracy and integrity of evidence, or copies of evidence.
Examining or analyzing the evidence: Using sound scientific methods to determine the characteristics of the evidence, conducting comparison for individuation of evidence, and conducting event reconstruction.
Presentation of findings: Interpreting the output from the examination and analysis based on findings of fact and articulating these in a format appropriate for the intended audience (e.g., court brief, executive memo, report).
Note on returning the evidence to the Owner/Victim
The final destination of most types of evidence is back with its original owner. Some types of evidence, such as
drugs or drug paraphernalia (i.e., contraband), are destroyed after the trial.
Any evidence gathered during a search, although maintained by law enforcement, is legally under the control of the courts. And although a seized item may be yours and may even have your name on it, it might not be returned to you unless the suspect signs a release or after a hearing by the court. Unfortunately, many victims do not want to go to trial; they just want to get their property back.
Many investigations merely need the information on a disk to prove or disprove a fact in question; thus, there is no need to seize the entire system. Once a schematic of the system is drawn or photographed, the hard disk can be removed and then transported to a forensic lab for copying.
Mirror copies of the suspect disk are obtained using forensic software and then one of those copies can be returned to the victim so that business operations can resume.
Reference(s) used for this question:
KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, Chapter 9: Law, Investigation, and Ethics (page 309).
and
The Official Study Book, Second Edition, Page 529-230
NEW QUESTION 22
Which of the following protocols does not operate at the data link layer (layer 2)?
- A. PPP
- B. RARP
- C. L2F
- D. ICMP
Answer: D
Explanation:
ICMP is the only of the mentioned protocols to operate at the network layer (layer 3). Other protocols operate at layer 2.
Source: WALLHOFF, John, CBK#2 Telecommunications and Network Security (CISSP Study Guide), April 2002 (page 1).
NEW QUESTION 23
Which of the following is required in order to provide accountability?
- A. Authentication
- B. Integrity
- C. Confidentiality
- D. Audit trails
Answer: D
Explanation:
Accountability can actually be seen in two different ways:
1) Although audit trails are also needed for accountability, no user can be accountable for their actions unless properly authenticated.
2) Accountability is another facet of access control. Individuals on a system are responsible for their actions. This accountability property enables system activities to be traced to the proper individuals. Accountability is supported by audit trails that record events on the system and network. Audit trails can be used for intrusion detection and for the reconstruction of past events. Monitoring individual activities, such as keystroke monitoring, should be accomplished in accordance with the company policy and appropriate laws. Banners at the log-on time should notify the user of any monitoring that is being conducted.
The point is that unless you employ an appropriate auditing mechanism, you don't have accountability. Authorization only gives a user certain permissions on the network. Accountability is far more complex because it also includes intrusion detection, unauthorized actions by both unauthorized users and authorized users, and system faults. The audit trail provides the proof that unauthorized modifications by both authorized and unauthorized users took place. No proof, No accountability.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, Page 50.
The Shon Harris AIO book, 4th Edition, on Page 243 also states:
Auditing Capabilities ensures users are accountable for their actions, verify that the secutiy policies are enforced,
and can be used as investigation tools. Accountability is tracked by recording user, system, and application activities.
This recording is done through auditing functions and mechanisms within an operating sytem or application.
Audit trail contain information about operating System activities, application events, and user actions.
NEW QUESTION 24
Which of the following is a tool often used to reduce the risk to a local area network (LAN) that has external connections by filtering Ingress and Egress traffic?
- A. a firewall.
- B. dial-up.
- C. passwords.
- D. fiber optics.
Answer: A
Explanation:
The use of a firewall is a requirement to protect a local area network (LAN) that has external connections without that you have no real protection from fraudsters.
The following answers are incorrect:
dial-up. This is incorrect because this offers little protection once the connection has been established.
passwords. This is incorrect because there are tools to crack passwords and once a user has been authenticated and connects to the external connections, passwords do not offer protection against incoming TCP packets.
fiber optics. This is incorrect because this offers no protection from the external connection.
NEW QUESTION 25
Which of the following would assist the most in Host Based intrusion detection?
- A. audit trails.
- B. access control lists.
- C. security clearances.
- D. host-based authentication.
Answer: A
Explanation:
To assist in Intrusion Detection you would review audit logs for access violations.
The following answers are incorrect:
access control lists. This is incorrect because access control lists determine who has access to what but do not detect intrusions.
security clearances. This is incorrect because security clearances determine who has access to what but do not detect intrusions.
host-based authentication. This is incorrect because host-based authentication determine who have been authenticated to the system but do not dectect intrusions.
NEW QUESTION 26
......
Recommend!! Get the Full SSCP dumps in VCE and PDF From Certleader, Welcome to Download: https://www.certleader.com/SSCP-dumps.html (New 1074 Q&As Version)
